CHAPTER
1-1
Cisco Video Surveillance 2500 Series IP Camera User Guide
OL-19273-02
1
Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the Cisco Video Surveillance IP Cameras and its features. It
includes these topics:
• Features, page 1-1
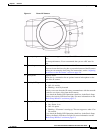
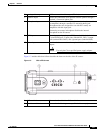
• IP Camera Physical Details, page 1-2
Features
The Cisco Video Surveillance IP Cameras offer a feature-rich digital camera solution for a video
surveillance system. They provide high-quality, bandwidth-efficient video capture and transmission,
with support for D1 resolution, motion-triggered viewing, and MPEG-4 encoding. The IP camera is
available in models for use in wired and wireless networks. The wired model can be powered through an
external power adapter or by integrated Power over Ethernet (PoE); the wireless model requires an
external power adapter and does not support PoE.
In addition, the devices provide networking and security capabilities, including multicast support,
hardware-based Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), hardware-based Data Encryption
Standard/Triple Data Encryption Standard (DES/3DES) encryption, and for the wireless IP camera,
802.1X authentication.
The IP camera includes the following key features:
• Built-in MPEG4 encoder—An internal MPEG4 encoder can generate up to two video streams.
• Built-in MJPEG encoder—An internal MJPEG encoder can generate the primary or secondary
video stream.
• Day/night switch support—An IR-cut filter provides increased sensitivity in low-light conditions.
• Two-way audio communication—Audio can be encoded with the video. With the internal or
optional external microphone and optional external speaker, you can communicate with people at
the IP camera location while you are in a remote location and viewing images from the IP camera.
• Multi-protocol support—Supports these protocols: DHCP, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, NTP, RTP, RTSP,
SMTP, SSL/TLS, and TCP/IP.
• Web-based management—You perform ongoing administration and management of the IP camera
through web-based configuration menus.
• Motion detection—The IP camera can detect motion in up to three designated fields of view by
analyzing changes in pixels and generate an alert if motion is detected.
• Flexible scheduling—You can configure the IP camera to respond to events that occur within a
designated schedule.