9-38
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual, R7.2
Chapter 9 Management Network Connectivity
9.7.8 IP-over-CLNS Tunnels
•
FT-TD
•
T-TD
•
LAN subnet
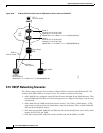
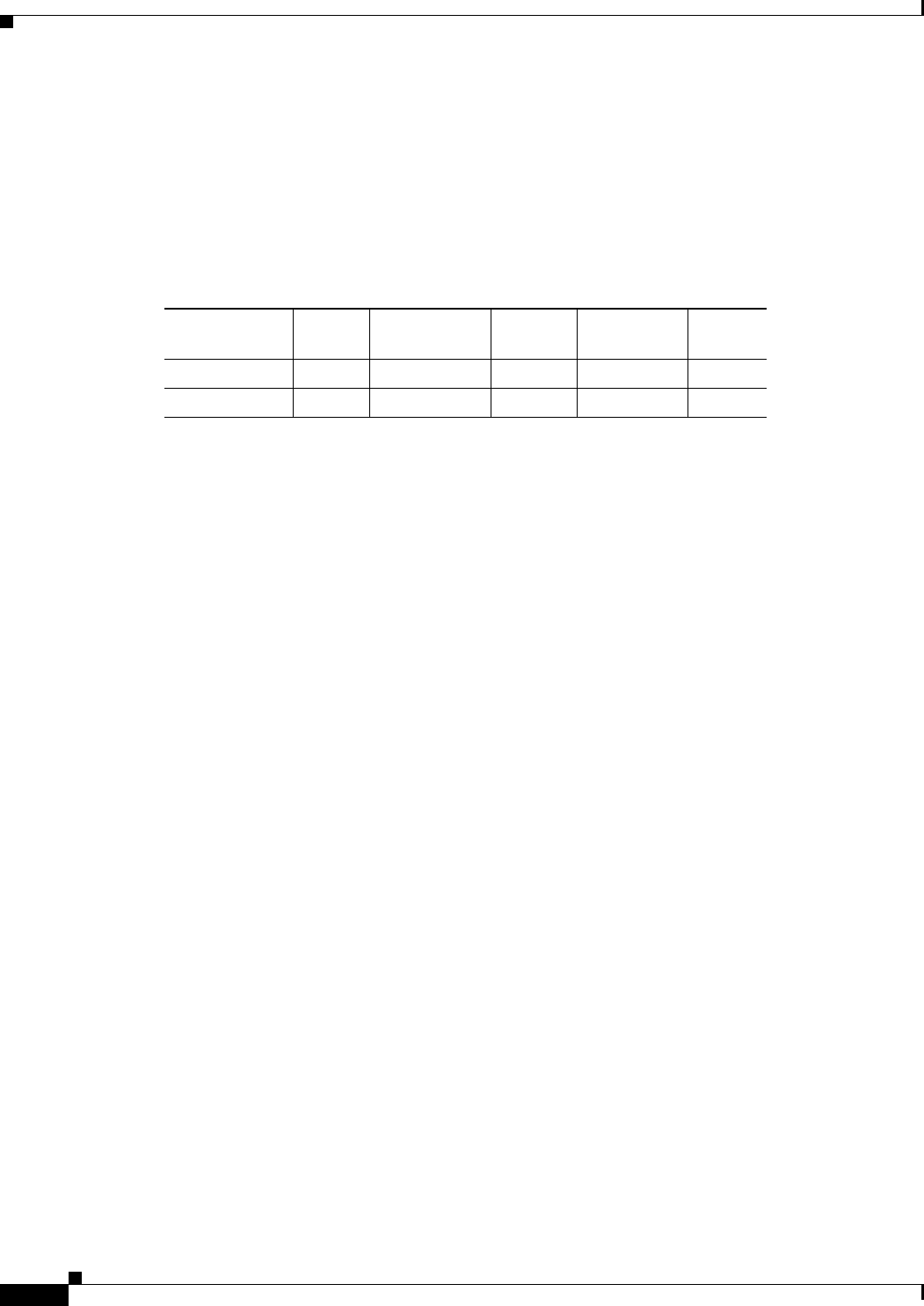
OSI virtual router constraints depend on the routing mode provisioned for the node. Table 9-14 shows
the number of IS L1s, IS L1/L2s, and DCCs that are supported by each router. An IS L1 and IS L1/L2
support one ES per DCC subnet and up to 100 ESs per LAN subnet.
Each OSI virtual router has a primary manual area address. You can also create two additional manual
area addresses. These manual area addresses can be used to:
•
Split up an area—Nodes within a given area can accumulate to a point that they are difficult to
manage, cause excessive traffic, or threaten to exceed the usable address space for an area.
Additional manual area addresses can be assigned so that you can smoothly partition a network into
separate areas without disrupting service.
•
Merge areas—Use transitional area addresses to merge as many as three separate areas into a single
area that shares a common area address.
•
Change to a different address—You might need to change an area address for a particular group of
nodes. Use multiple manual area addresses to allow incoming traffic intended for an old area address
to continue being routed to associated nodes.
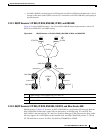
9.7.8 IP-over-CLNS Tunnels
IP-over-CLNS tunnels are used to encapsulate IP for transport across OSI NEs. The ONS 15600 supports
two tunnel types:
•
GRE—Generic Routing Encapsulation is a tunneling protocol that encapsulates one network layer
for transport across another. GRE tunnels add both a CLNS header and a GRE header to the tunnel
frames. GRE tunnels are supported by Cisco routers and some other vendor NEs.
•
Cisco IP—The Cisco IP tunnel directly encapsulates the IP packet with no intermediate header.
Cisco IP is supported by most Cisco routers.
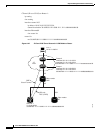
Figure 9-25 shows the protocol flow when an IP-over-CLNS tunnel is created through four NEs (A, B,
C, and D). The tunnel ends are configured on NEs A and D, which support both IP and OSI. NEs B and
C only support OSI, so they only route the OSI packets.
Table 9-14 OSI Virtual Router Constraints
Routing Mode Router 1 Router 2 — 12
IS L1
per area
IS L1/L2
per area
DCC
per IS
IS L1 Yes Yes 250 — 60
IS L1/L2 Yes Yes 250 50 60