10-6
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual, R7.2
Chapter 10 Ethernet Operation
10.4.3 VLAN
The bridge sends bridge packets to the PPP half-bridge, which converts them to routed packets and
forwards them to other router processes. Likewise, the PPP half-bridge converts routed packets to
Ethernet bridge packets and sends them to the bridge on the same Ethernet subnetwork.
The ASAP line card is transparent to any Layer 2 and above protocol packets (the entire control plane).
Any PPP Half Bridge control packets are transported out to the SONET interface.
10.4.3 VLAN
The ASAP line card is transparent to VLAN tag information in the Ethernet frame.
Note
VLANs are tunneled, and not terminated.
10.5 Buffering and Flow Control
Because the STS circuits can often be oversubscribed (have a bandwidth lower than that needed to
support the traffic on the Ethernet port), a combination of buffering and local flow control is supported.
Initially, frames that arrive on an ingress interface that cannot be transmitted immediately on the egress
interface are placed in an ingress buffer. When this buffer starts filling up and is in danger of
overflowing, flow control is employed. Local flow control is flow control between the Ethernet interface
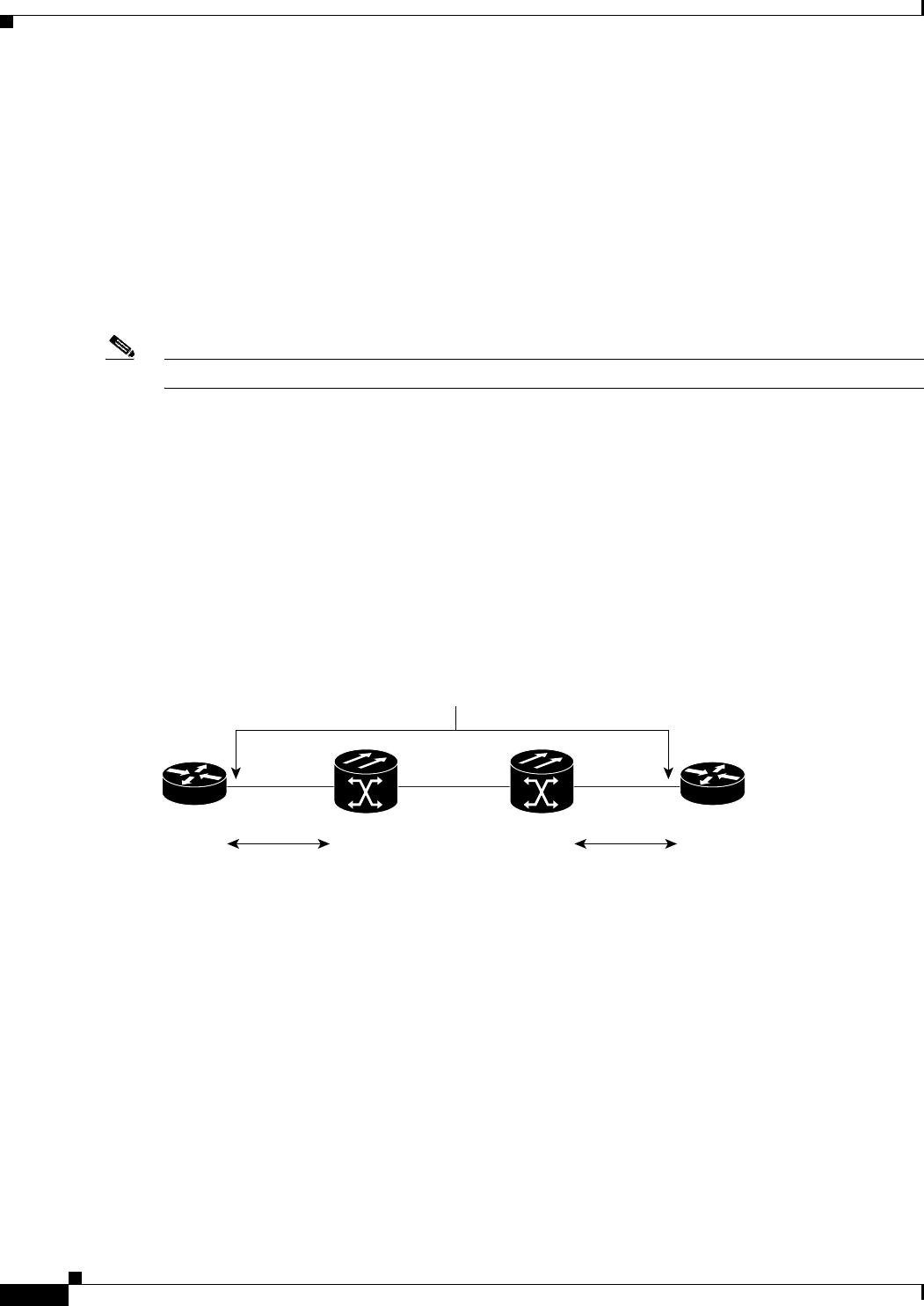
and the router or switch it is connected to, over the single Ethernet link. This is depicted in Figure 10-3.
Figure 10-3 Buffering and Flow Control
To prevent dropping of frames on an ingress Ethernet interface due to buffer congestion, an Ethernet
interface sends a PAUSE frame to its peer on its egress Ethernet interface. An Ethernet interface might
be capable of both sending and receiving PAUSE frames (symmetric flow control). On the other hand, it
might be capable of performing only one of the two (asymmetric flow control). Two factors determine
what an Ethernet interface ultimately ends up supporting:
•
Flow control capability of the interface as provisioned by the operator (fixed at OFF or ON)
•
Flow control capability of the peer as determined by AutoNegotiation
The Ethernet interfaces are capable of using symmetric or asymmetric flow control to meter packet
receptions according to the requirements specified in IEEE 802.3x. This is done to avoid dropping
packets internally due to output or input queue congestion. When an Ethernet interface uses symmetric
124485
Ethernet links
Flow Control
- PAUSE
frames
SONET network
Router Router
15xxx 15xxx
Flow Control
- PAUSE
frames