C156-E097-01EN 7 - 15
Implementation of the ARBITRATION phase is a system option. This phase is required for
system that has two or more INITs or uses the RESELECTION phase. The procedure to obtain
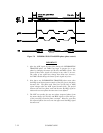
control of the SCSI bus is as follows (see Figure 7.6):
1) The SCSI device shall wait for a BUS FREE phase (see Subsection 7.5.1).
2) The SCSI device shall wait at least 800 ns (Bus Free Delay) after Bus Free phase detection.
3) Then the SCSI device that arbitrates the bus asserts the DATA BUS bit corresponding to its
own SCSI ID and BSY signal within 1.8 µs (Bus Set Delay) after last observation of the
BUS FREE phase (*1).
4) After waiting at least 2.4 µs (Arbitration Delay) since the SCSI device asserted the BSY
signal, the SCSI device shall examine the value on the DATA BUS to determine the priority
of the bus arbitration. (The priority of the bus arbitration is in the descending order of data
bus bit numbers; the highest priority is DB7 (ID#7) and the lowest priority is DB0 (ID#0)).
• When the SCSI device detects any ID bit which is assigned higher priority than its own
SCSI ID, the SCSI device shall release its signals (BSY and its SCSI ID), then may
return to step 1). (The SCSI device #1 in Figure 7.6 has lost the arbitration.)
• The SCSI device which detects no higher SCSI ID bit on the DATA BUS can obtain the
bus control, then it shall assert SEL signal. (The SCSI device #7 in Figure 7.6 has won
the arbitration.)
• Any other SCSI device that is participating in the ARBITRATION phase shall release
its signals within 800 ns (Bus Clear Delay) after the SEL signal becomes true, then may
return to step 1). (The SCSI device #3 in Figure 7.6 has lost the arbitration.)
5) The SCSI device which wins arbitration (SCSI device #7 in Figure 7.6) shall wait at least 1.2
µs (Bus Clear Delay + Bus Settle Delay) after asserting the SEL signal before changing any
signal state.
*1: When an SCSI device sends its SCSI ID to the DATA BUS, it asserts only the bit at the
position corresponding to its own ID and leaves the other seven bits false. The parity bit
(DBP signal) is not driven or is driven true, rather than false. The parity bit on the DATA
BUS is unpredictable during an ARBITRATION phase.