High-Quality AVCHD Recording, Plus the Professional PH Mode Boosts the Quality of HD Images
AVCHD Format for High-
Quality, Efficient HD
Recording
Panasonic AVCCAM
camcorders use the AVCHD
format for tapeless recording
with high image quality and
low bit rates. This format
complies with the latest
H.264 motion image
compression standard, and
employs the High Profile
standard to improve
compression efficiency.
Featuring twice the
compression efficiency of
HDV (MPEG-2), the
AG-HMC150 series achieves
extended HD recording. The
following four new
technologies make this
possible.
MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 Technologies
Intra-Frame Prediction
This process generates predictive pixels based on the adjacent pixels
within each frame. It then selects the optimal predictive mode. The
generated predictive image is subtracted from the original input image,
and the residual data is compressed and recorded at a low bit rate.
The entire process is conducted within the frame, so prediction
accuracy remains high even with fast-motion images.
Variable Block Size Motion Compensation
In contrast with MPEG-2, in which inter-frame compression based on
the correlation between adjacent frames uses fixed blocks of 16 x 16
pixels, AVCHD divides the blocks into multi-sizes as small as 4 x 4
pixels. In this method, it is able to use large blocks to process images
that show only slight changes on the screen, and smaller blocks to
process images that have considerable change. This raises the
accuracy of motion compensation to boost the quality of fast-motion
images while increasing compression efficiency.
Loop Filter Prevents the Propagation of Compression Distortion
Because MPEG-2 uses a decoding image that contains compression-
induced block distortion as a reference image for motion
compensation, it exhibits residual distortion — even within the same
frame — when a large amount of block distortion is generated.
MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 detects block distortion in the decoding image
and removes it with a context-adaptive filter that functions according
to the degree of distortion. This prevents the propagation of block
distortion by keeping the reference image clean at all times.
New CABAC Entropy Encoding
The AVCHD format uses CABAC (Context Adaptive Binary Arithmetic
Coding) for its variable-length encoding. Compared with the variable-
length encoding of MPEG-2, in which the compression efficiency is
greatly affected by subject type, CABAC provides lossless
compression with constantly high efficiency and no distortion for
virtually all subject types. Because MPEG-2 compresses and converts
data according to the standard's fixed conversion rules, the
compression efficiency may drop for image types other than those that
were considered when the standard was established. In place of fixed
conversion rules, CABAC provides the best possible conversion
method by constantly optimizing and automatically tracking the image
that is being processed, in parallel with the compression process.
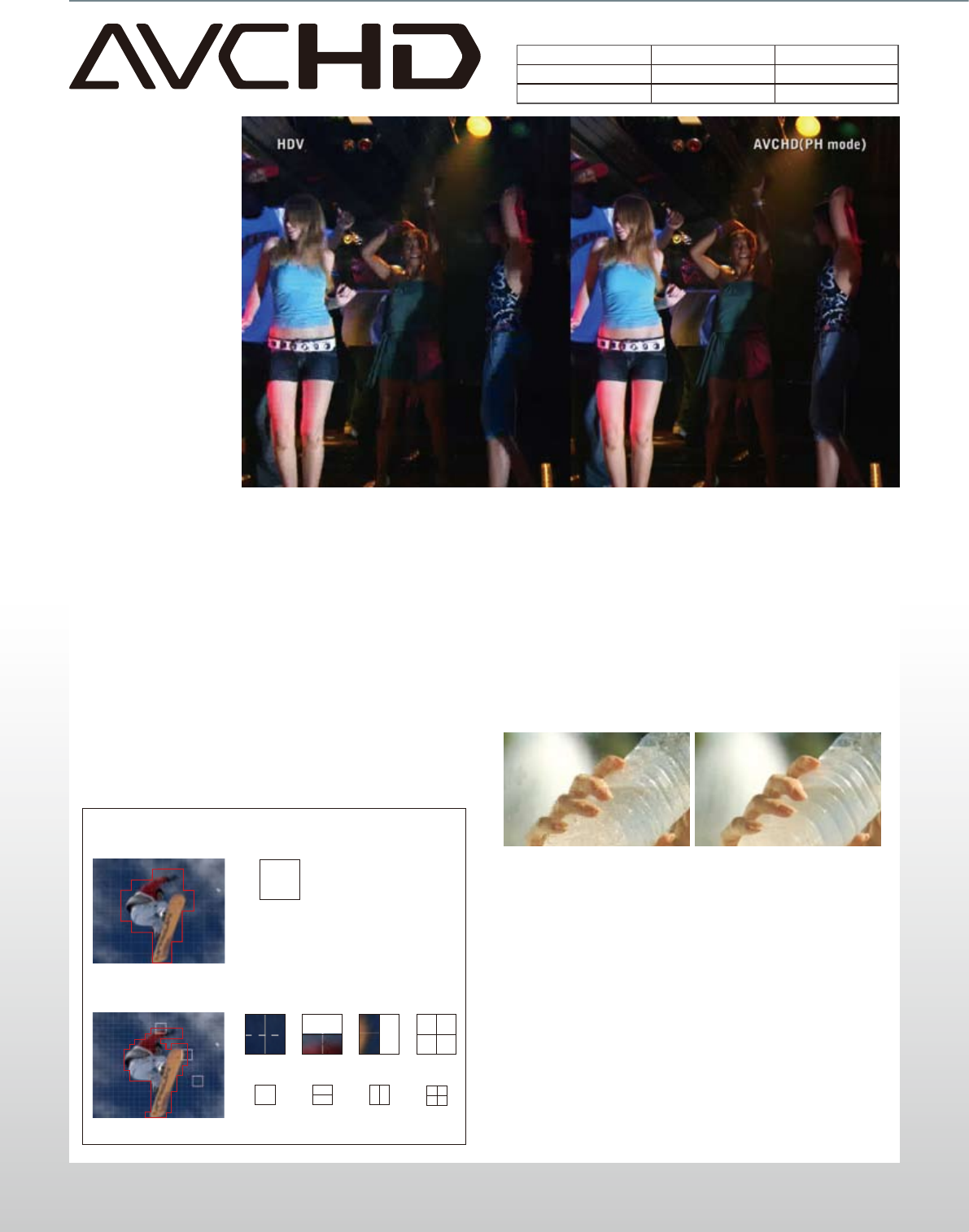
HDV AVCHD
Pixel (H x V) 1440 x 1080 1920 x 1080
Compression Method
MPEG-2 MPEG-4 AVC/H.264
Comparison of HD Recording Formats
Sample comparison: When a flash causes large contrast differences and reduces depth perception, HDV shows considerable block noise, while AVCHD in the
PH mode minimize break-up.
MPEG-2 (fixed block size)
Blocks of the same size are used to process parts both with and without motion.
MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 (variable block size)
Block size is precisely varied to match the size of the moving part contained in each block.
16×16
16×16
16×8 8×16 8×8
8×8 8×4 4×8 4×4
MPEG-2 MPEG-4 AVC/H.264














