Chapter 7 Menu Displays and Detailed Settings
131
7-3 Adjustments and Settings from Menus
4
To end the menu operation, set the MENU ON/OFF
switch to OFF.
7-3-10Using UMID Data
To perform operations from interviewing to editing
effectively and to detect audio-visual materials easily
when reusing them, metadata that provides additional
information is recorded along with audio-visual data on a
disc. As one of application of metadata, the UMID
(Unique Material Identifier) is internationally
standardized.
What is a UMID?
The UMID (Unique Material Identifier) is a unique
identifier for audio-visual material defined by the
SMPTE330M-2003 standard.
The UMID may be used either as the 32-byte Basic UMID
or as the extended UMID, which includes an additional 32
bytes of Source Pack to make a total 64 bytes.
For details, refer to SMPTE 330M.
Globally unique ID is automatically recorded every
shooting.
The Extended UMID is metadata that provides additional
information such as location, time/date, company and so
on.
The UMID is applied as follows.
Using the Extended UMID
You have to enter a country code, organization code and
user code. Set the country code referring to the ISO-3166
table, and set the organization code and user code
independently.
19 FORMAT
16:9/4:3 SELECT : 16:9
SCAN MODE : PsF
UC/J SELECT : UC
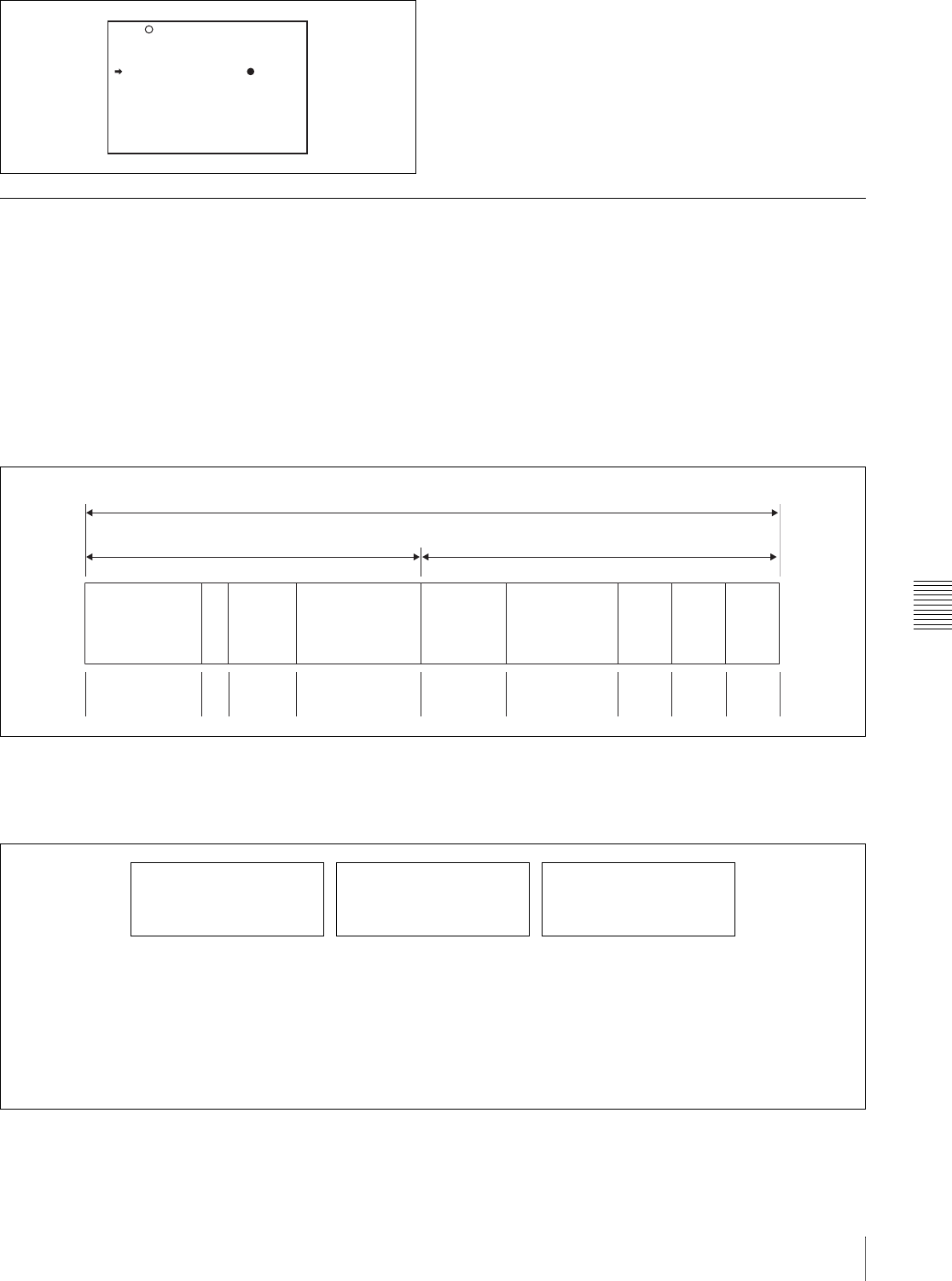
Extended UMID (64 bytes)
Basic UMID (32 bytes) Source Pack (32 bytes)
Universal label L Inst. No. Material Number Time/Date
Spatial
Co-ordinates
Country Org User
12 bytes 1 3 bytes 16 bytes 8 bytes 12 bytes 4 bytes 4 bytes 4 bytes
Instance No.
Material No.
ID generated when shooting
Same as the above
Source Pack
Shooting information (when,
where and who)
Same as the above
M
Distinguishing between the
original material and copied
material
M
Material source ID/detecting
material
M
Metadata pack that identifies
the source of material unit by
defining the when, where
and who of the material unit
with which it is associated.
Original material: 00 00 00
Copied material: generation number
(1 byte) + random number (2 byte)


















