Nodal Point (continued)
Step 2: Fore-Aft Adjustment
This step is most easily
accomplished out of doors. Find
a vertical edge or line, such as a
doorway or edge of a building.
Position your camera and tripod
about 2-1/2 feet away, or as close
as possible with the edge still in
focus when you look through
the viewfinder. If you’re using
a multirow head such as the
QuickPan III Spherical, set the
swing arm to a level horizontal
position (zero degrees).
Looking through the camera’s
viewfinder, find another vertical
edge or line that is far away, such
as another building or telephone
pole. Align the two objects and
rotate the pan head so they are in
the left hand side of the viewfinder.
Rotate the pan head so the two
objects move over to the right
hand side of the viewfinder. Unless
you’ve managed to unwittingly
locate the right position, you
should notice the two objects will
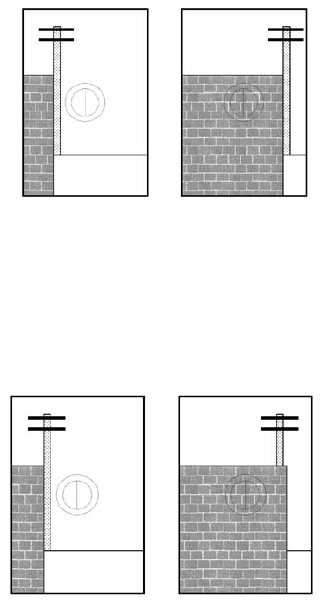
If, as shown above, the two objects move with respect to one
and another in the viewinder, slide the camera fore or aft in
order to eliminate this movement. Here, the telephone pole
has moved behind the brick wall.
move with respect to each other
as you rotate the pan from left to
right. Slide the camera to the front
or rear as required to eliminate
this relative movement.
Step 3: Record Your Results
After you’ve discovered the two
location dimensions, be sure to
record the settings. The QuickPan
III has convenient indicator
scales for this purpose. These
numbers represent the nodal
point for this given camera and
lens combination. If you change
cameras or lenses, this procedure
may have to be repeated
Step 5: How About Rangefinder
Cameras?
A rangefinder camera is a
camera where you look through
a separate viewfinder and not
through the actual lens. The
process is basically the same.
Locate the Side-to-Side adjustment
as discussed in Step 1. When it
What is it and how do I find it?
Looking through the viewfinder align a close object (brick wall)
with a faraway object (telephone pole). As you rotate the camera
from side-to-side there should be no relative movement between
the two objects as shown to the right.


















