5
●
When both JPEG and MPEG4 images are distributed
When both JPEG and MPEG4 images are distributed,
distribution works in the same way as frame rate priority
mode if the distribution request would be accepted in the
frame rate priority mode. If the distribution request would
be denied in the frame rate priority mode, the frame rate
is controlled such that the maximum bit rate is as shown
in the following table, to accept distribution requests for
up to a total number of 20 JPEG and MPEG distributions.
However, distribution requests for which the total bit rate
of the MPEG4 distribution stream exceeds 10 Mbps will
be denied.
Maximum JPEG bit rate when only JPEG and MPEG4
data is distributed
When only MPEG4 images are distributed, the maximum
number of distributions is determined by the preset bit
rate. When a distribution request that exceeds the
maximum number of distributions is received, this
request is denied.
When distributing only MPEG4 data (
A
Page 4)
Memo:
● If the bit rate is changed when image
distribution is in progress, the restriction on
distribution may not work correctly.
Insufficient network bandwidth
When there is insufficient bandwidth, the number
of JPEG frames (frame rate) that the client can
acquire will decrease. Delay will also occur in the
distribution of images. In the case of MPEG4,
noise interference may occur and playback may
fail. There may be a longer delay or interruption
in the audio.
Network Delay
When the client acquires JPEG via TCP,
camera
will send out data while checking the ACK from
the client at the same time. For networks with
considerable delay, data cannot be sent out until
ACK is received, and therefore the frame rate
will drop. In the case of MPEG4, noise
interference may occur and playback may fail.
Audio may be interrupted.
Decrease in the frame rate due to network delays
can be eliminated by receiving data via multicast.
Network Jitter
When there is considerable network jitter, delay
time may be prolonged and the image frame rate
may drop. In the case of MPEG4, noise
interference may occur and playback may fail.
Audio may be interrupted.
Packet Loss
When acquiring images from
camera
via TCP,
packet loss may be recovered by TCP
transmission. When there is considerable delay
in the network, however, missing data may occur
and the image frame rate may drop. In the case
of MPEG4, noise interference may occur and
playback may fail.
Audio may be interrupted.
When packet loss occurs during multicast
sending from
camera
, the image frame rate may
drop. In the case of MPEG4, noise interference
may occur and playback may fail.
Audio may be interrupted.
List of Protocols and Port Numbers
Used by camera
camera
uses the protocols and port numbers
listed below. Ensure that these ports are allowed
through the firewall when a firewall is to be
installed.
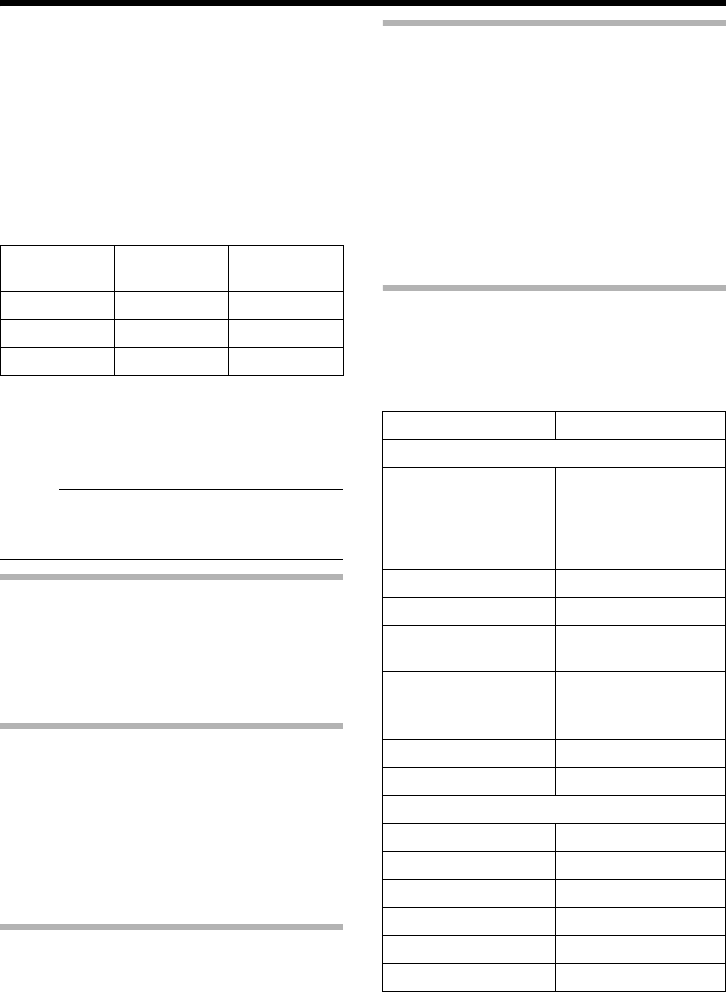
Current number
of distributions
Maximum bit rate
Total maximum
bit rate
2 and below 5 Mbps 10 Mbps
3 to 4 2.5 Mbps 10 Mbps
5 to 20 0.5 Mbps 10 Mbps
Protocol/Port No. Purpose of Use
Source
TCP/80 JPEG/MPEG4
acquisition, Web
Settings page, API,
Sending/Acquisition
of sound
TCP/5510 VSIP
UDP/5510 VSIP
UDP/9541 VSIP discovery
protocol
TCP/10020
TCP/10021
TCP/10023
(Reserved for
adjustment)
TCP/32040 Alarm server
TCP/49298 Sound data reception
Destination
TCP/20, 21 FTP
TCP/25 Mail delivery
TCP/110 POP (Mail Delivery)
TCP/User Setting No. Sending alarm
UDP/123 SNTP
UDP/User Setting No. Sending alarm


















