Philips Pixel Defect Policy
Philips strives to deliver the highest quality products. We use some of the industry's most
advanced manufacturing processes and practice stringent quality control. However, pixel or
sub pixel defects on the TFT LCD panels used in flat panel monitors are sometimes
unavoidable. No manufacturer can guarantee that all panels will be free from pixel defects,
but Philips guarantees that any monitor with an unacceptable number of defects will be
repaired or replaced under warranty. This notice explains the different types of pixel defects
and defines acceptable defect levels for each type. In order to qualify for repair or
replacement under warranty, the number of pixel defects on a TFT LCD panel must exceed
these acceptable levels.
This policy is valid worldwide.
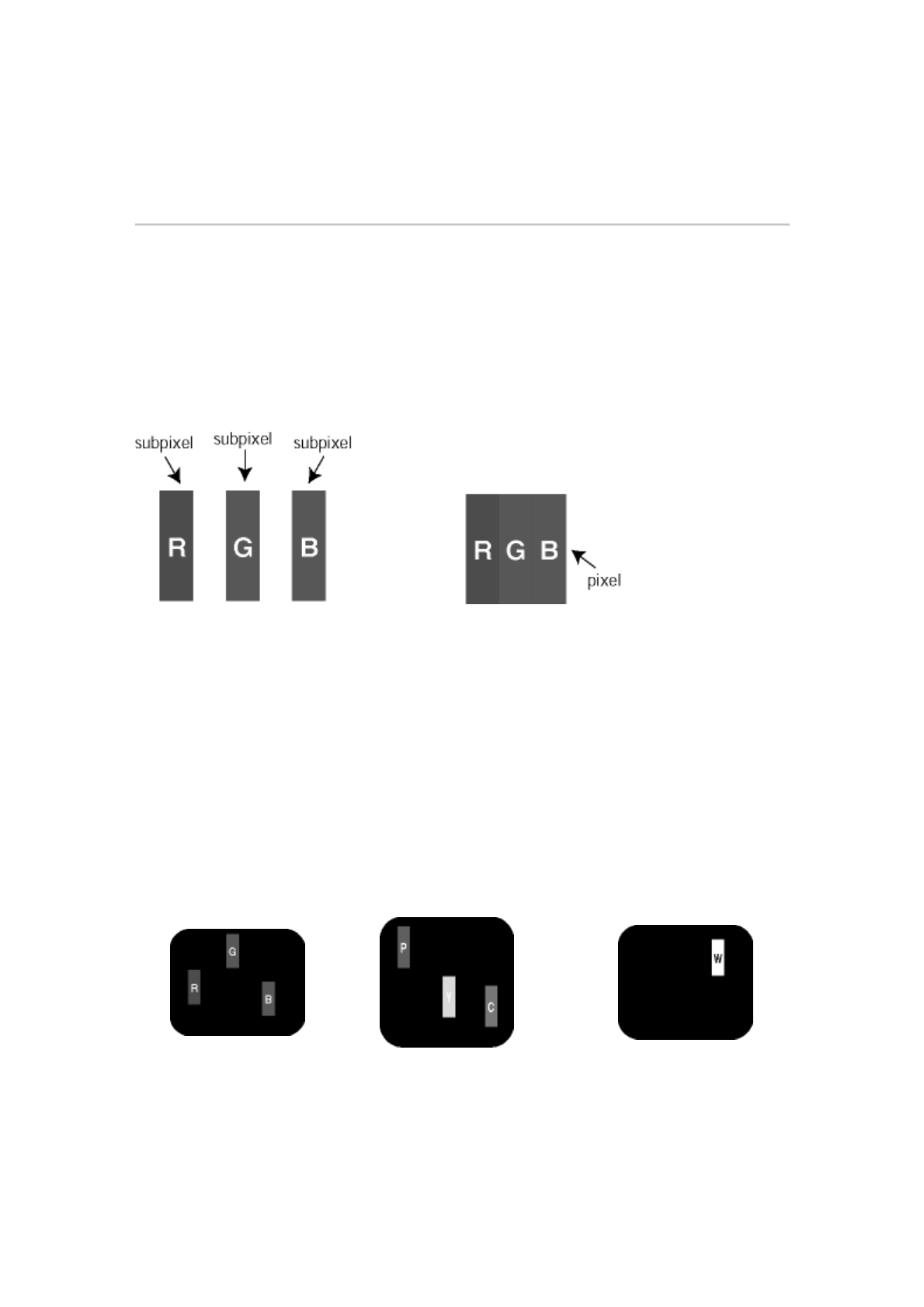
Pixels and Sub pixels
A pixel, or picture element, is composed of three sub pixels in the primary colors of red,
green and blue. Many pixels together form an image. When all sub pixels of a pixel are lit,
the three colored sub pixels together appear as a single white pixel. When all are dark, the
three colored sub pixels together appear as a single black pixel. Other combinations of lit
and dark sub pixels appear as single pixels of other colors.
Types of Pixel Defects
Pixel and sub pixel defects appear on the screen in different ways. There are two categories
of pixel defects and several types of sub pixel defects within each category.
Bright Dot Defects Bright dot defects appear as pixels or sub pixels that are always lit or
'on'. That is, a bright dot is a sub-pixel that stands out on the screen when the monitor
displays a dark pattern. There are the types of bright dot defects:
One lit red, green or blue
sub pixel
Two adjacent lit sub pixels:
- Red + Blue = Purple
- Red + Green = Yellow
- Green + Blue = Cyan (Light Blue)
Three adjacent lit sub
pixels (one white pixel)
A red or blue bright dot must be more than 50 percent brighter than neighboring
dots while a green bright dot is 30 percent brighter than neighboring dots.


















