Chapter 5 Performing Machine Vision Tasks
© National Instruments Corporation 5-9 IMAQ Vision for Visual Basic User Manual
Defining Regions Programmatically
When you have an automated application, you need to define regions of
interest programmatically. You can programmatically define regions by
providing basic parameters that describe the region you want to define. You
can specify a rotated rectangle by creating a CWIMAQRotatedRectangle
object and setting the coordinates of the center, width, height, and rotation
angle. You can specify an annulus by creating a CWIMAQAnnulus object
and setting the coordinates of the center, inner radius, outer radius, start
angle, and end angle. You can specify a point by setting its x-coordinates
and y-coordinates. You can specify a line by setting the coordinates of the
start and end points.
Refer to Chapter 3, Making Grayscale and Color Measurements, for more
information about defining regions of interest.
Find Measurement Points
After you set regions of inspection, locate points in the regions on which
you can base measurements. You can locate measurement points using
edge detection, pattern matching, color pattern matching, and color
location.
Finding Features Using Edge Detection
Use the edge detection tools to identify and locate sharp discontinuities
in an image. Discontinuities typically represent abrupt changes in pixel
intensity values, which characterize the boundaries of objects.
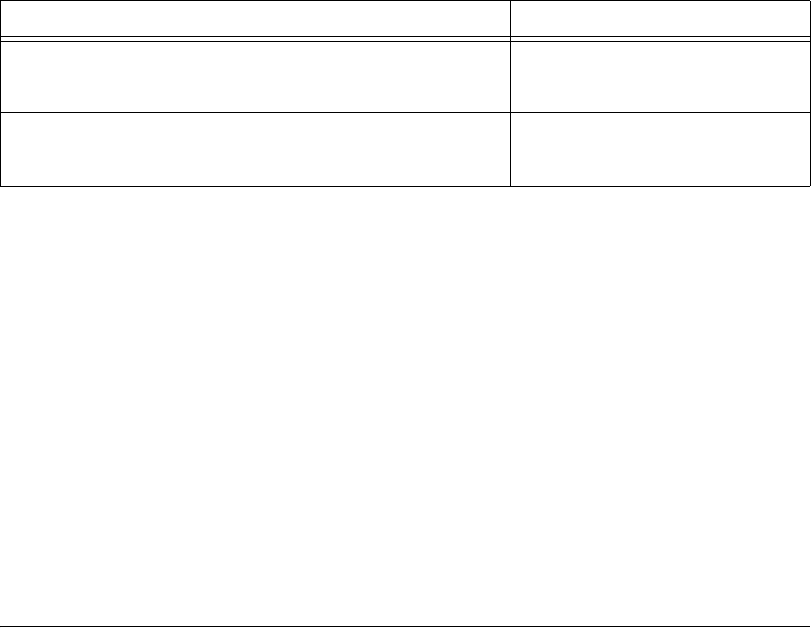
SetupViewerForPointSelection
GetSelectedPointFromViewer
LightMeterPoint
SetupViewerForLineSelection
GetSelectedLineFromViewer
LightMeterLine
Table 5-1. ROI Selection Methods to Use with CWMachineVision Methods (Continued)
CWMachineVision ROI Selection Methods CWMachineVision Method


















