27
Camera Settings
When taking pictures, you may simply use the default settings which have already been chosen
for use with your digital camera. But if you want to have more control over the quality of your
pictures and customize how you want to use your digital camera, you may adjust the various
camera settings to suit your needs.
Specifically, your digital camera allows you to do the following:
Select the desired camera sensitivity.
Adjusting exposure compensation.
Adjust the white balance when taking pictures under different lighting conditions.
Choose the desired quality and resolution for your pictures.
Control the use of the LCD monitor and power of your camera.
Specify basic settings such as language, date and time.
Enable the Self-Timer.
Camera settings can be accessed from the following three menus: Picture, Camera, and Setup
menus. The Capture ( ), Sports ( ) , and Burst ( ) modes all share the same menus
and settings.
This section describes the camera settings underneath each of the three menus in detail. If you
are not familiar yet on how to access camera menus, refer to "Navigating through Menus" in the
"Getting Started" section for information on how to display menu screens and choose settings.
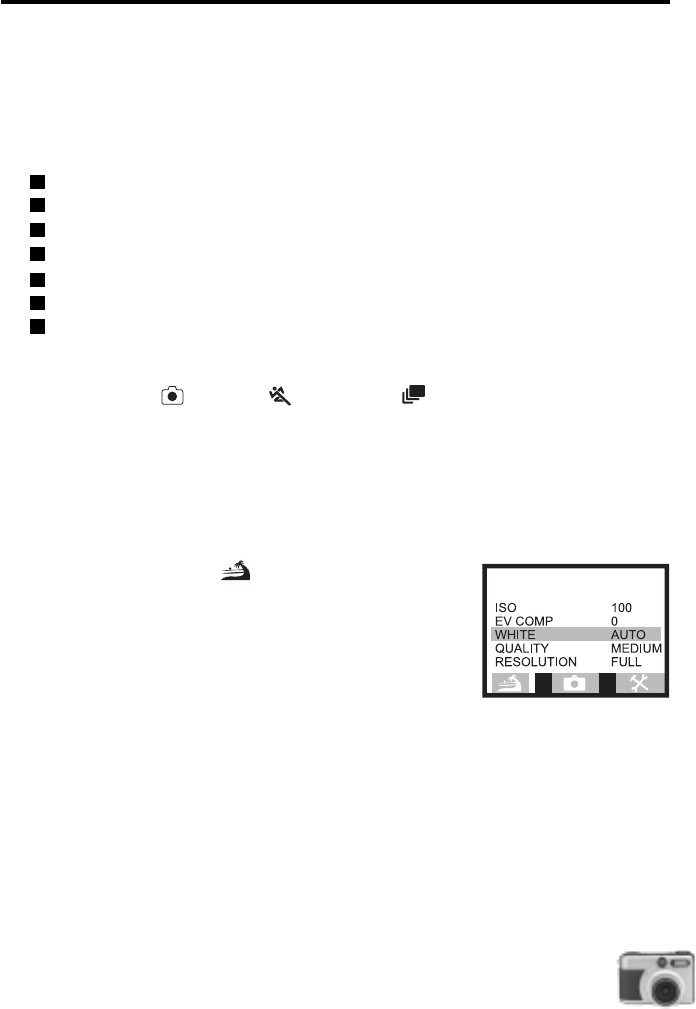
The Picture Menu ( )
If you want to improve picture results, go to the Picture Menu
and adjust its option settings. In this menu, you will modify the
following settings: ISO, Exposure Compensation, White Balance,
Picture Quality, Picture Resolution.
ISO (Sensitivity)
Three camera sensitivity settings can be selected : ISO 100, 200 and 400. The numeric values
are based on an ISO equivalent. ISO is the standard used to indicate film sensitivity, the higher
the number, the more sensitive the film, the more noise the image.
Exposure Compensation
Pictures may turn out underexposed if the subject is backlit (that is, the light source is behind the
subject) or when you are photographing under extremely bright lighting. To avoid having


















