11
4 Common Configuration Scenarios
This section provides configuration examples for three common deployments of the adaptive security
appliance:
• Hosting a web server on a DMZ network
• Establishing remote-access VPN connections so that off-site clients can establish secure
communications with the internal network
• Establishing a site-to-site VPN connection with other business partners or remote offices
Use these scenarios as a guide when you set up your network. Substitute your own network addresses
and apply additional policies as needed.
Scenario 1: DMZ Configuration
A demilitarized zone (DMZ) is a separate network located in the neutral zone between a private
(inside) network and a public (outside) network. This example network topology is similar to most
DMZ implementations of the adaptive security appliance. The web server is on the DMZ interface,
and HTTP clients from both the inside and outside networks can access the web server securely.
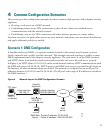
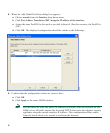
In Figure 4, an HTTP client (10.10.10.10) on the inside network initiates HTTP communications with
the DMZ web server (10.30.30.30). HTTP access to the DMZ web server is provided for all clients on
the Internet; all other communications are denied. The network is configured to use an IP pool of
addresses between 10.30.30.50 and 10.30.30.60. (The IP pool is the range of IP addresses available to
the DMZ interface.)
Figure 4 Network Layout for DMZ Configuration Scenario
DNS
server
132064
Internet
T
TP client
HTTP client
HTTP serve
r
Security
Appliance
.168.1.2
e address)
inside interface
192.168.1.1
(private address)
outside interface
209.165.200.225
(public address)
DMZ interface
10.30.30.1
(private address)
DMZ Web
Server
Private IP address: 10.30.30.30
Public IP address: 209.165.200.225