Q. How to assure accurate temperature measurement?
A. A solid understanding of infrared technology and its principles lies behind
accurate temperature measurement. When the temperature is measured by a non-
contact device the IR energy emitted from the measured object passes through the
optical system of the thermometer or thermal imager and is converted to an electrical
signal at the detector. This signal is then displayed as a temperature reading and/ or
thermal image. There are several important factors that determine accurate
measurement. The most important factors are emissivity, distance to spot ratio, and
field- of-view.
Emissivity
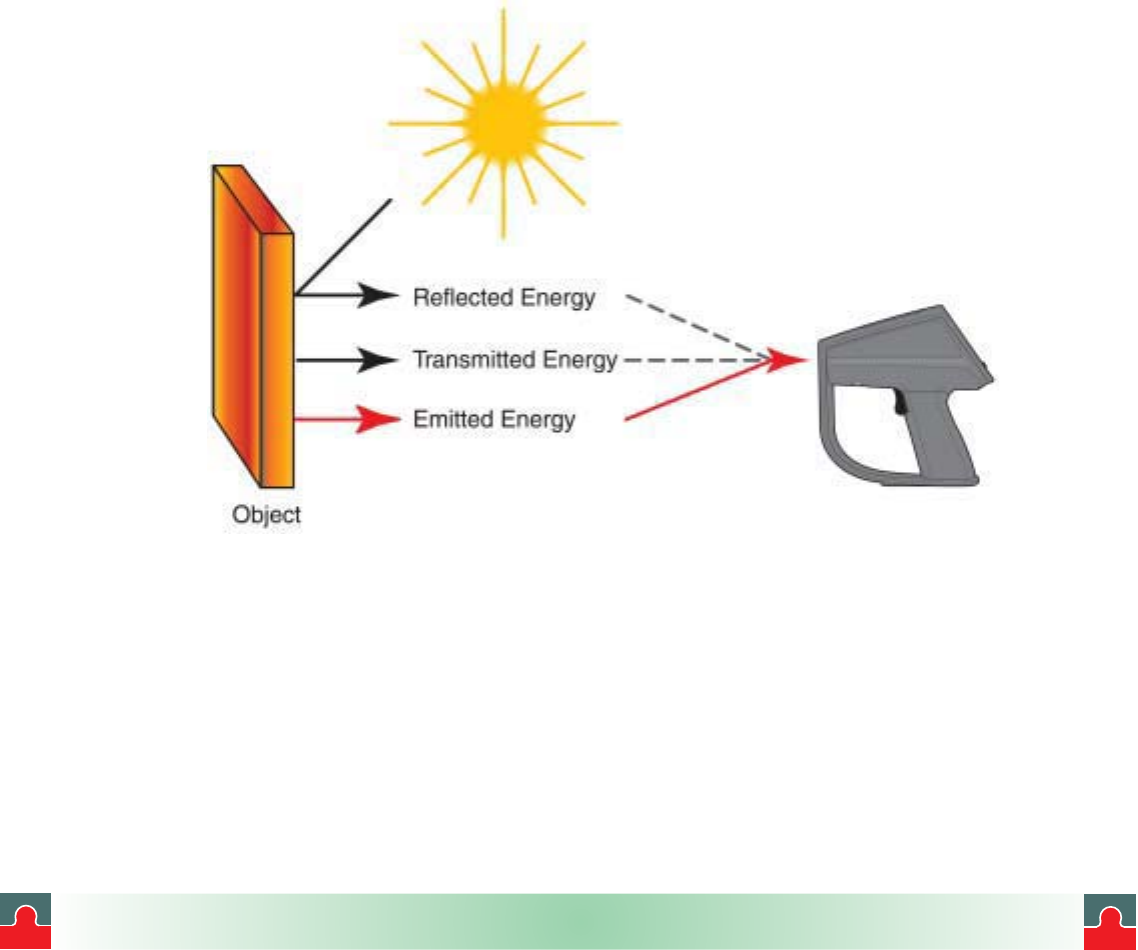
All objects reflect, transmit and emit energy. Only the emitted energy indicates the
temperature of the object. When IR thermometers or thermal imagers measure the
surface temperature they sense all three kinds of energy, therefore all thermometers
have to be adjusted to read emitted energy only. Measuring errors are often caused
by IR energy being reflected by light sources.
Some IR thermometers and thermal imagers allow you to change the emissivity in
the unit. The value of emissivity for various materials can be looked up in published
emissivity tables.
Other units have a fixed, pre-set emissivity of 0.95, which is the emissivity value for
most organic materials and painted or oxidized surfaces. If you are using a
thermometer or thermal imager with a fixed emissivity to measure the surface
July 1, 2003 - 72 - Version 1.0
i
i
Tel: (01943) 602001- WWW.ISSLTD.CO.UK - Fax: (01943) 816796