6. Appendices
48
Gray Scale Scanning
Glay Scale scanning converts an original into image data consisting of 4-bit or 8-bit gradations.
Four bits can express 16 gradations, and eight bits can express 256 gradations. This function is
used to output an original that contains intermediate tones on an output device that can express
intermediate tones for a single pixel, such as a display or a Dye Sublimation printer.
Although a higher number of bits produces higher image quality, it is important to remember that
the processing time will be longer. For example, when an area is scanned using the 8-bit multi-
scan mode, it requires eight times as much memory as when scanning the same area through
binary scanning or halftone scanning.
Limitation
❒ When this function is used during duplex scanning, there are limits on the front and image
data size: 3.6 million bytes with gray scale scanning, and 4 million bytes with binary
scanning
❒ During double-sided scanning, this function is valid only for the front side of the original.
data size for the reverse side is 360 million bytes.
Note
❒ When using this function, the image on the reverse side might be scanned through the
document, depending on the condition of the original.
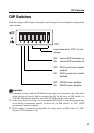
180 LPI70 LPI 95 LPI
Original 4-bit image
8-bit image