120
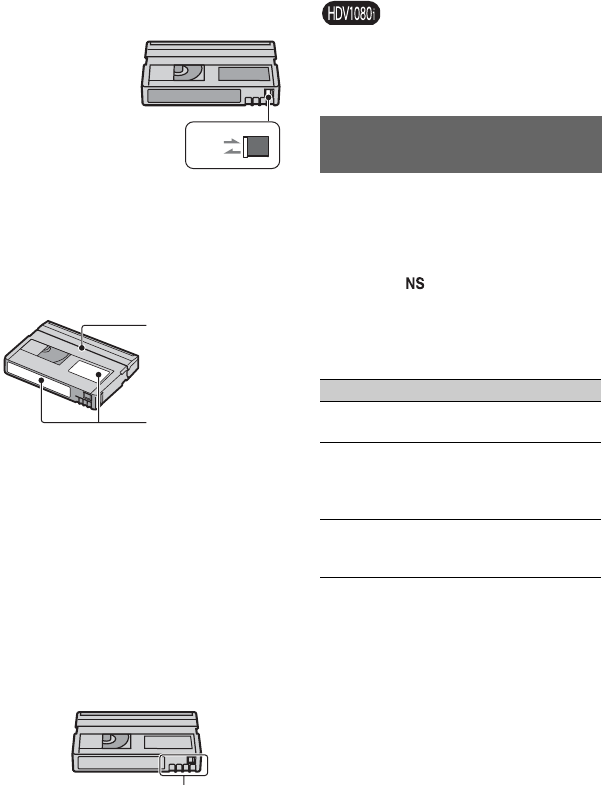
x To prevent accidental erasure
Slide the write-protect tab on the cassette to
set it to SAVE.
x When labeling the cassette
Be sure to place the label only on the
locations shown in the following
illustration so as not to cause a malfunction
of your camcorder.
x After using the cassette
Rewind the tape to the beginning to avoid
distortion of the picture or the sound. The
cassette should then be put in its case, and
stored in an upright position.
x When cleaning the gold-plated
connector
Generally, clean the gold-plated connector
on a cassette with a cotton-wool swab after
every 10 times it has been ejected.
If the gold-plated connector on the cassette
is dirty or dusty, the remaining tape
indicator may not show correctly.
On Sony HDV1080i compliant TVs
An HDV format compatible TV with the
component input jack is required to view
playback pictures recorded in the HDV
format.
The DVCAM format was developed as a
more reliable and higher-end format than
the consumer DV format. Explained here
are the differences, compatibility, and
limitations on editing for the DVCAM and
DV formats.
appears when the DVCAM
standard is not met.
Differences between the DVCAM and
DV formats
* There are 2 modes for audio recording, lock
mode and unlock mode. In lock mode, the
sampling frequencies of audio and video are
synchronized. Therefore, lock mode is more
effective than unlock mode in digital
processing and smooth transition during audio
editing.
REC
SAVE
REC: The cassette can be
recorded.
SAVE: The cassette cannot be
recorded (write-protected).
Do not put a label
along this border.
Labeling position
Gold-plated connector
Compatibility of the DVCAM/DV
formats
Specification DVCAM DV
TRACK
Pitch
15 µm 10 µm
Audio
sampling
frequency
12 bit:32
kHz
16 bit:48
kHz
12 bit:32 kHz
16 bit:48 kHz
44.1 kHz
48 kHz
Audio
recording
mode*
Lock mode Lock/Unlock
mode
Maintenance and precautions (Continued)


















