INFORMATION
TRANSFER phase
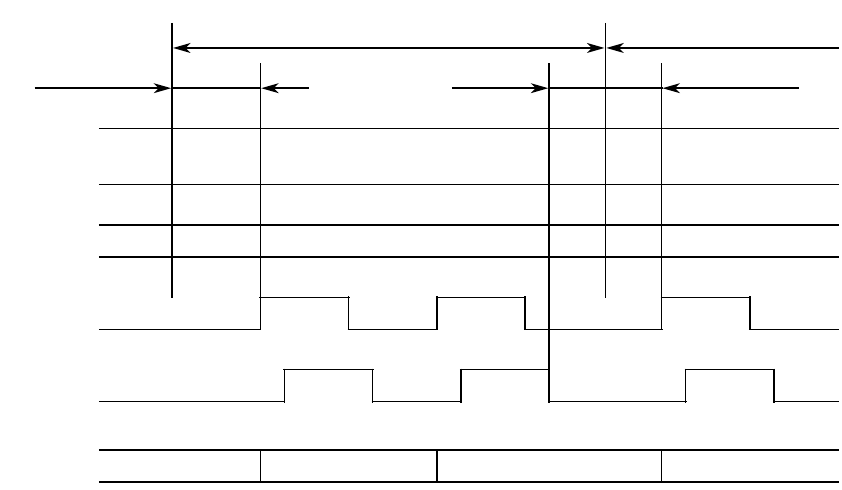
Min. 0ns bus settle delaybus settle delay
INFORMATION TRANSFER phase
BSY
SEL
C/D,
MSG, I/O
REQ
ACK
DB
The INFORMATION TRANSFER phases use one or more REQ/ACK handshakes to
control the information transfer. Each REQ/ACK handshake allows the transfer of
one byte of information. During the INFORMATION TRANSFER phases the BSY
signal shall remain true and the SEL signal shall remain false. Additionally,
during the INFORMATION TRANSFER phases, the target shall continuously
envelope the REQ/ACK handshake (s) with the C/D, I/O, and MSG signals in such a
manner that these control signals are valid for a bus settle delay before the
assertion of the REQ signal of the first handshake. These control signals remain
valid until after the negation of the ACK signal at the end of the handshake of the
last transfer of the phase.
(1) Asynchronous information transfer
The target shall control the direction of information transfer by means of the I/O
signal. When the I/O signal is true, information shall be transferred from the target
to the initiator. When the I/O signal is false, information shall be transferred from
the initiator to the target.
a. Asynchronous transfer from target to initiator
If the I/O signal is true (transfer to the initiator), the target shall first drive the
DB(7>0, P) signals to their desired values, delay at least one deskew delay plus a
cable skew delay then assert the REQ signal. The DB(7>0, P) signals shall
remain valid until the ACK signal is true at the target. The initiator shall read
the DB(7>0, P) signals after the REQ signal is true then indicate its acceptance
of the data by asserting the ACK signal. When the ACK signal becomes true at
the target, the target may change or release the DB(7>0, P) signals and shall
negate the REQ signal. After the REQ signal is false, the initiator shall then
negate the ACK signal.
4 $ 18