Network Video Server User’s Guide
64
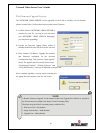
H. Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS)
Your internet Service Provider (ISP) provides you at least one IP address which you use to connect
to the Internet. The address you get may be static, meaning it never changes, or dynamic, meaning
it’s likely to change periodically. Just how often it changes, depends on your ISP. A dynamic IP
address complicates remote access since you may not know what your current WAN IP address is
when you want to access your network over the Internet. The solution to the dynamic IP address
problem comes in the form of a dynamic DNS service.
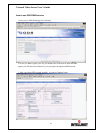
The Internet uses DNS servers to lookup domain names and translates them into IP addresses.
Domain names, such as www.intellinet-network.com, are just easy to remember aliases for IP
addresses. A dynamic DNS service is unique because it provides a means of updating your IP
address so that your listing will remain current when your IP address changes. There are several
excellent DDNS services available on the Internet and best of all they’re free to use. Two DDNS
services are www.ods.org
(ODS) and www.DynDNS.org. You’ll need to register with the service
and set up the domain name of your choice to begin using it. Please refer the home page or the
service for detailed instructions.
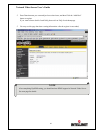
A DDNS service works by uploading your WAN IP address to its servers periodically, your
gateway-router may support DDNS directly, in which case you can enter your DDNS account
information into your router and it will update the DDNS servers automatically when your IP
address changes. Please consult your router’s documentation for more information. If your router
does not support DDNS, you can run a small client utility on any PC on your network which will
perform the updating. The client utility is usually provided for free by the service.
Check the service’s web page for further information, terms and conditions.