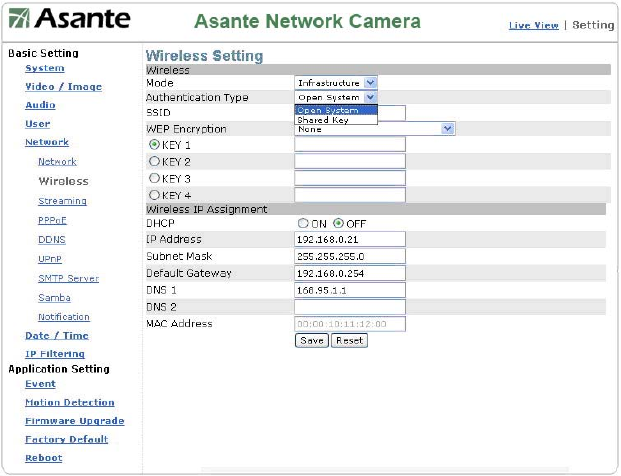
Shared Key Authentication
Shared key authentication relies on the fact that both stations taking part in the authentication
process have the same "shared" key or pass phrase. The shared key is manually set on both
the client station and the AP/router. Three types of shared key authentication are available
today for home or small office WLAN environments.
SSID: An SSID is the public name of a wireless network. You will use this to connect a
trusted wireless AP.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
The process consists of an authentication request from the client, clear challenge text from the
AP/router, encrypted challenge text from the client and an authentication response from the
AP/router. Two levels for WEP keys/pass phrases:
1. 64-bit: 40 bits dedicated to encryption and 24 bits allocated to Initialization Vector (IV). It
may also be referred to as 40-bit WEP.
2. 128-bit: 104 bits dedicated to encryption and 24 bits allocated to Initialization Vector
(IV). It may also be referred to as 104-bit WEP.
WEP security mode: Select an encryption mode from the list. The format is “None” by default,
indicating that the security function is disabled.
Authentication mode: One of the following authentication modes is required when you select
a WEP encryption mode from the security list.
1. 64 Bit (10 Hex chars)
2. 64 Bit (5 ASCII chars)
3. 128 Bit (26 Hex chars)
4. 128 Bit (26 ASCII chars)
WEP key password encryption mode:
You can set up 64 Bit or 128 Bit WEP key password encryption mode. A set of 64 Bit
encryptions is equivalent to 10 sets of hexadecimal digits or 5 sets of ASCII characters. A set
©2007 Asante Networks Inc., All rights reserved. NetCam are registered trademarks of Asante Network, Inc.
All other names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Specifications subject to change without prior notice.
39


















