AXIS 211M - System Options
27
802.1X - Network Admission Control
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE standard for port-based Network Admission Control. It provides authentication to
devices attached to a network port (wired or wireless), establishing a point-to-point connection, or, if
authentication fails, preventing access on that port. 802.1X is based on EAP (Extensible Authentication
Protocol).
In an 802.1X enabled network switch, clients equipped with the correct software can be authenticated and
allowed or denied network access at the Ethernet level.
Clients and servers in an 802.1X network may need to authenticate each other by some means. In the Axis
implementation this is done with the help of digital certificates provided by a Certification Authority. These are
then validated by a third-party entity, such as a RADIUS server, examples of which are FreeRADIUS and
Microsoft Internet Authentication Service.
To perform the authentication, the RADIUS server uses various EAP methods/protocols, of which there are
many. The one used in the Axis implementation is EAP-TLS (EAP-Transport Layer Security).
The AXIS network video device presents its certificate to the network switch, which in turn forwards this to the
RADIUS server. The RADIUS server validates or rejects the certificate and responds to the switch, and sends its
own certificate to the client for validation. The switch then allows or denies network access accordingly, on a
preconfigured port.
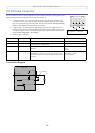
The authentication process
1. A CA server provides the required signed certificates.
2. The Axis video device requests access to the protected network at the network switch. The switch
forwards the video device’s CA certificate to the RADIUS server, which then replies to the switch.
3. The switch forwards the RADIUS server’s CA certificate to the video device, which also replies to the
switch.
4. The switch keeps track of all responses to the validation requests. If all certificates are validated, the
Axis video device is allowed access to the protected network via a preconfigured port.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) - AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting)
protocol for applications such as network access or IP mobility. It is intended to work in both local and roaming
situations.
CA servers - In cryptography, a Certification Authority (CA) is an entity that provides signed digital certificates
for use by other parties, thus acting a trusted third party. There are many commercial CA’s that charge for their
services. Institutions and governments may have their own CA, and there are free CA’s available.
Date & Time
Current Server Time - displays the current date and time (24h clock). The time can be displayed in 12h clock
format in the Overlay (see below).
New Server Time - Select your time zone from the drop-down list. If you want the server clock to automatically
adjust for daylight savings time, select the Automatically adjust for daylight saving time changes.
From the Time Mode section, select the preferred method to use for setting the time:
• Synchronize with computer time - sets the time from the clock on your computer.
• Synchronize with NTP Server - the camera will obtain the time from an NTP server every 60 minutes.
The NTP Server can be set under Network > TCP/IP > Advanced or click on the No server specified
link, see NTP Configuration, on page 29.
• Set manually - this option allows you to manually set the time and date.
Date & Time Format Used in Images - specify the formats for the date and time (12h or 24h) displayed in the
video streams.