Chris Admin can export a directory containing only the database files with statistics
of the bridge construction safety records. This operation can be performed without
fear of unknown users accessing the sensitive data. Chris Admin can use the export
command to allow only selected client systems to have access to the files. This
way, both groups of students will be able to mount and access the same data and
work with it on their separate, different workstations.
What File Systems Can I Export?
You can export any of the following file systems:
v “Root” (/)
v QOpenSys
v QSYS.LIB
v QDLS
v QOPT
v UDFS
You cannot export other file systems that have been mounted from remote servers.
This includes entire directory trees as well as single files. AS/400 follows the
general rules for exporting as detailed in “Rules for Exporting File Systems” on
page 28. This set of rules also includes the general NFS “downstream” rule for
exporting file systems. Remember that whenever you export a file system, you also
export all the directories and objects that are located hierarchically beneath
(“downstream” from) that file system.
The CHGNFSEXP or EXPORTFS command is the key for making selected portions
of the local user view part of the remote client view.
Exported file systems will be listed in the export table built from the /etc/exports
file. These file systems will be accessible to client mounting, assuming the client
has proper access authorities. Users will be able to mount and access exported
data as if it were local to their client systems. The administrator of the server can
also change the way file systems are exported dynamically to present remote
clients with a different view of file systems.
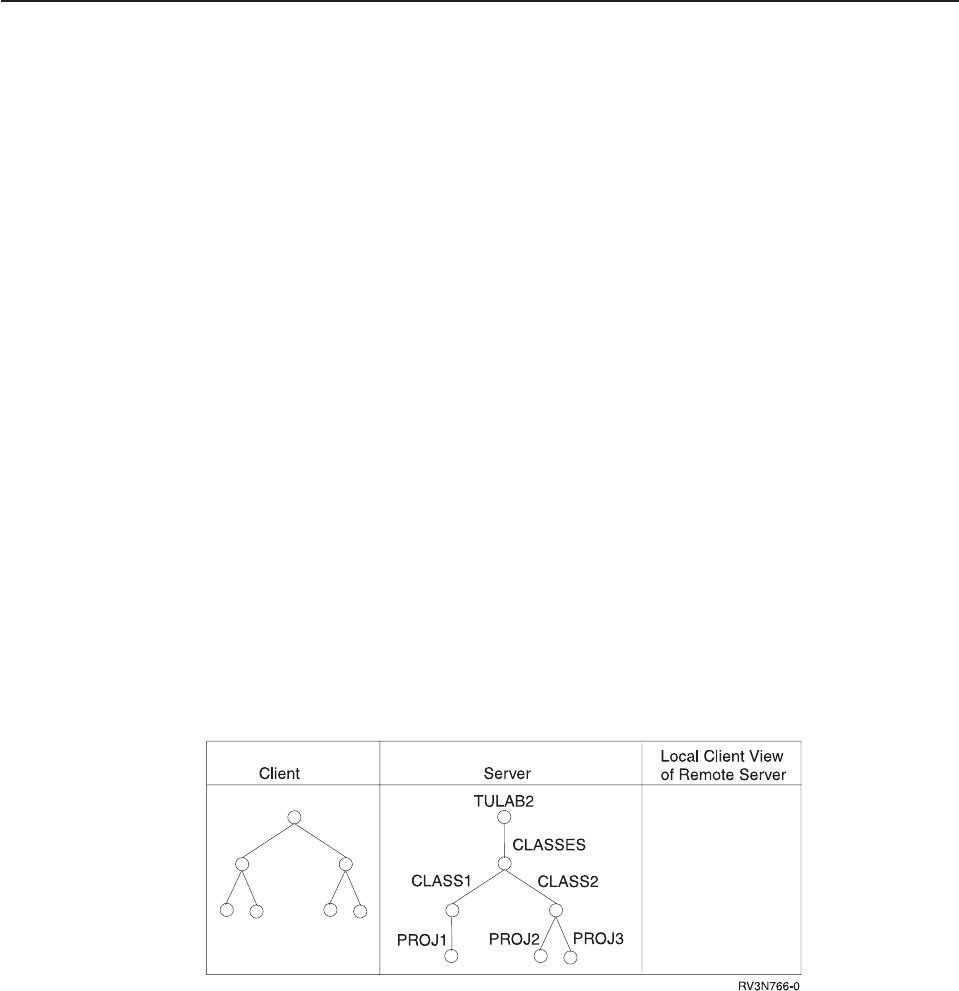
Before exporting, a remote client cannot view any local server file systems.
Figure 19. Before the server has exported information
Chapter 4. Server Exporting of File Systems 27