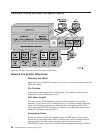
waits for requests (the standard is #2049). All server daemons will use this
same port. The NFS server daemons then wait on the port for RPC requests
from NFS clients to access local files.
4. The user starts the mount daemon (QNFSMNTD). This daemon registers to the
local RPC binder daemon. It then waits on the assigned port for RPC requests
from NFS clients to mount local file systems.
5. The user starts the NSM daemon (QNFSNSMD). It registers to the local RPC
binder daemon. It then waits on the assigned port for RPC requests to monitor
systems.
6. The user starts the NLM daemon (QNFSNLMD). It registers to the local RPC
binder daemon. It then waits on the assigned port for RPC requests to manage
locks.
If you specify *ALL for the SERVER parameter for the Start Network File System
Server (STRNFSSVR) command will automatically start all the daemons in the
correct order.
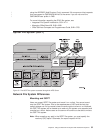
In a typical NFS client startup:
1. The user starts the RPC binder (port mapper) daemon, if it is not already
operational. On a given system, a single port mapper is used for both client and
server.
2. The user starts the block I/O daemon (QNFSBIOD) or daemons. This daemon
controls the caching of data and attributes that have been transmitted from the
server.
3. The user starts the NSM daemon, if it is not already operational. On a given
system, a single NSM operates for both the client and server.
4. The user starts the NLM daemon, if it is not already operational. On a given
system, a single NLM is used for both the client and server.
STRNFSSVR (Start Network File System Server) Command
Purpose
The Start Network File System Server (STRNFSSVR) command starts one or all of
the Network File System (NFS) server daemons.
You should use the SERVER(*ALL) option, which will start the daemons in the
following order, as well as call the export command. This order is the recommended
order for starting the Network File System.
v The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) binder daemon
v The block I/O (BIO) daemon
v call the export command
v The server (SVR) daemon
v The mount (MNT) daemon
v The network status monitor (NSM) daemon
v The network lock manager (NLM) daemon
If you are choosing to start just one daemon, be sure you understand the
appropriate order for starting NFS daemons and the possible consequences of
starting deamons in an order other than that specified above.
Chapter 7. NFS Startup, Shutdown, and Recovery 67