91
HISTOGRAM
The histogram is a graph depicting the distribution of brightness values in
the image for each of the three color channels (Red, Green, and Blue) (The
histogram displayed in the Quick Preview is the distribution of tones in the
image). The horizontal axis shows the brightness level, with darker pixels
towards the left side and brighter pixels toward the right. The vertical axis
shows the proportion of pixels at each level of brightness.
By examining the histogram of the full image, you can gauge the over-all
exposure of that image. You can also use the histogram to determine if
zoomed-in sections of an image are over or under exposed.
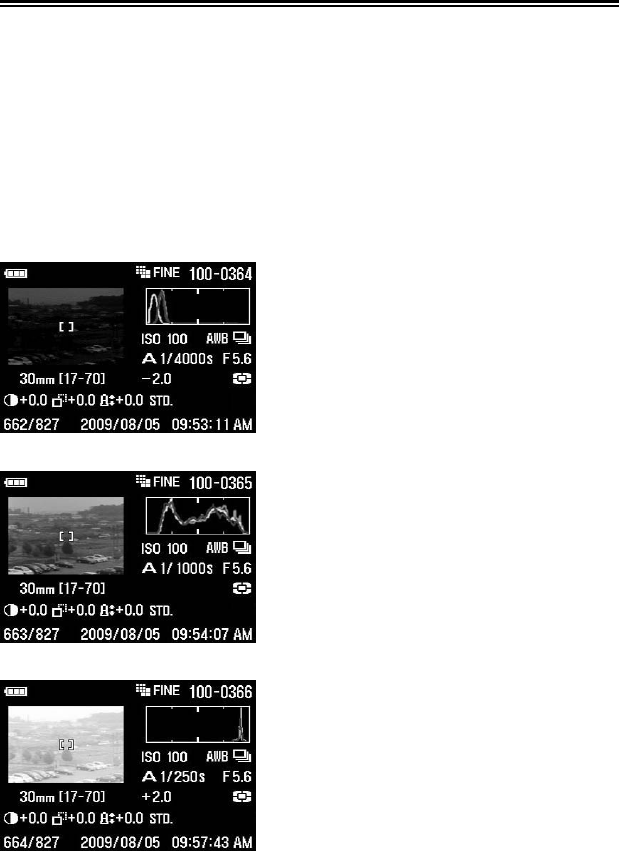
This histogram shows that the higher pixel
values are never used in the image,
indicating that the image is underexposed,
and therefore will appear dark. In general,
when the histogram is higher on the left side,
the image is mostly composed of dark pixels,
causing it to appear dark—either because
the image is underexposed or because it is a
dark scene such as night shot or sunset.
This histogram shows a fairly even
distribution of pixel values, indicating that the
image is well exposed, with good contrast.
However, the histogram distribution of a well
exposed image will vary greatly depending
on the subject.
This histogram shows that many of the pixel
values are at their brightness limit, indicating
that some areas of the image may be blown
out. In general, when the histogram runs off
the right side, the image will have many white
pixels—either because the image is
overexposed or because it is a bright scene
such as the beach or snow.


















