89
Shooting Functions
4
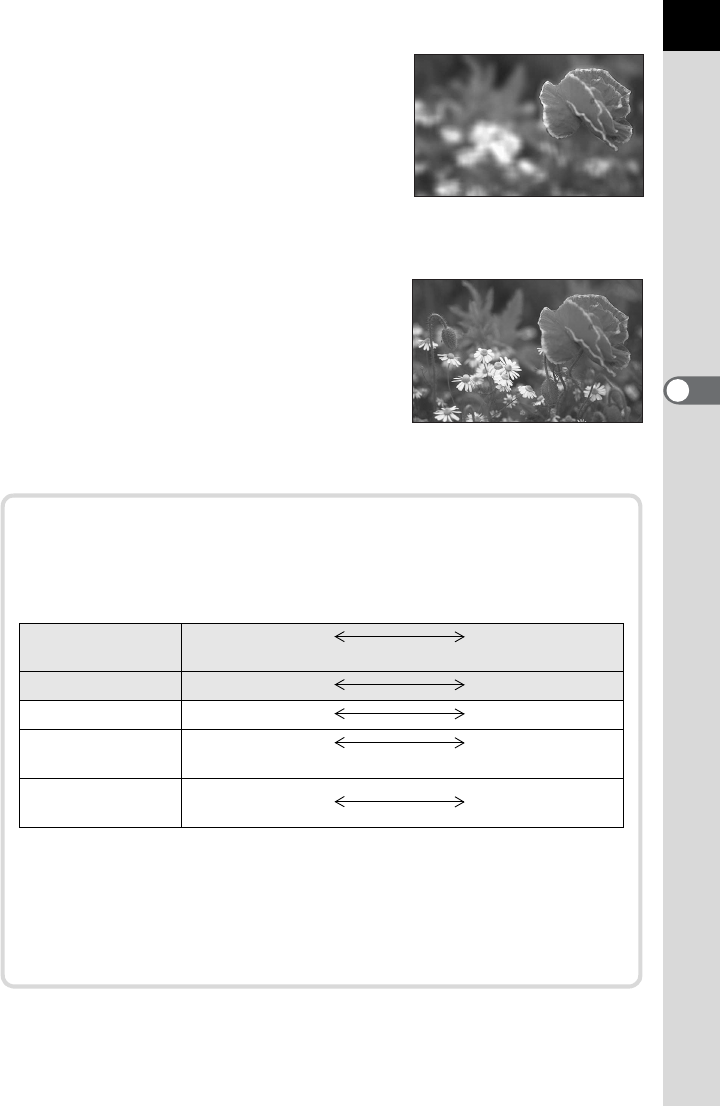
Opening the aperture (reduce the
aperture value)
Objects closer and farther than the
focused subject will be more out of focus.
For instance, if you take a picture of a
flower against a landscape with the
aperture open, the landscape in front and
behind the flower will be blurred,
emphasizing only the flower.
Closing the aperture (increase the
aperture value)
The range in focus expands forward and
backward. For instance, if you take a
picture of a flower against a landscape
with the aperture narrowed, the landscape
in front and behind the flower will be in
focus.
Aperture and Depth of Field
The following table summarizes how the aperture affects the depth of
field. The depth of field may also change depending on the lens used
and the distance to the subject.
• The depth of field for the Q differs depending on the lens but
compared to a 35 mm camera, the value is roughly one aperture
setting lower (the focused range becomes narrower).
• The wider the wide-angle lens, and the farther away the subject,
the deeper the depth of field is (some zoom lenses do not have a
scale for depth of field because of their designs).
Aperture
Open Close
(Smaller value) (Larger value)
Depth of field Shallow Deep
Area of focus Narrow Wide
Lens focal length
Longer Shorter
(Telephoto) (Wide-angle)
Distance to the
subject
Near Far


















