61
Appendix A: Router Configuration
Appendix A: Router Configuration
If you have signed up a consumer grade broadband service, and you use a router to
share your internet access, you will need to address following three major issues:
a. DDNS service
b. Port forwarding
c. Demilitarized Zone
If you are not familiar with those network terms, then you will probably need a network
technician to help to setup the iGuard.
The following information assumes you have basic knowledge about networking and
is for your reference only. Technical support for remote monitoring is only available
to those who subscribe to the DDNS service provided by Web Surveillance, LLC
a. DDNS:
In order to access the iGuard from internet, you will have to know the external IP
address of your iGuard. If you have a consumer grade broadband service, this IP
address may change over time, making it impossible for the remote PC to
communicate with your iGuard, just like you ask people to call you but you change
your phone number without notified the other party. The solution is to subscribe to a
DDNS service which keeps track of your IP address. iGuard is compatible with the
DDNS service offered by Web Surveillance, LLC (www.websurveillance.com
).
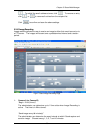
b. Port Forwarding
If you place the iGuard behind a router, you need to programme the router so that it
can direct the specific incoming traffic to iGuard.
By default iGuard uses Port 80 for HTTP traffic (web manager) and port 9001 for
video streaming. So you need forward port 80 traffic to the internal IP address of the
iGuard.
If your Internet service Provider blocks port 80/9001 or you already host a website on
the same network, you’ll need to reconfigure your iGuard and router to other ports
such as 81/9002, 82/9003, etc.
Note: The section you need to look for in the router is Port Forwarding or Virtual
Server
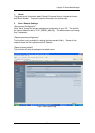
C. Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
iGuard uses port 9001 by default to stream video to the internet. Unfortunately this
port is normally disabled or blocked by most commercial router’s built-in firewall. In
order for the iGuard applications to work properly, the firewall settings in the router
need to be configured.
Some router has a very sophisticated built-in firewall. Instead of programming each
port on the router, you can use the DMZ feature to by-pass the firewall setting.