Configuring OSPF
8 - 5
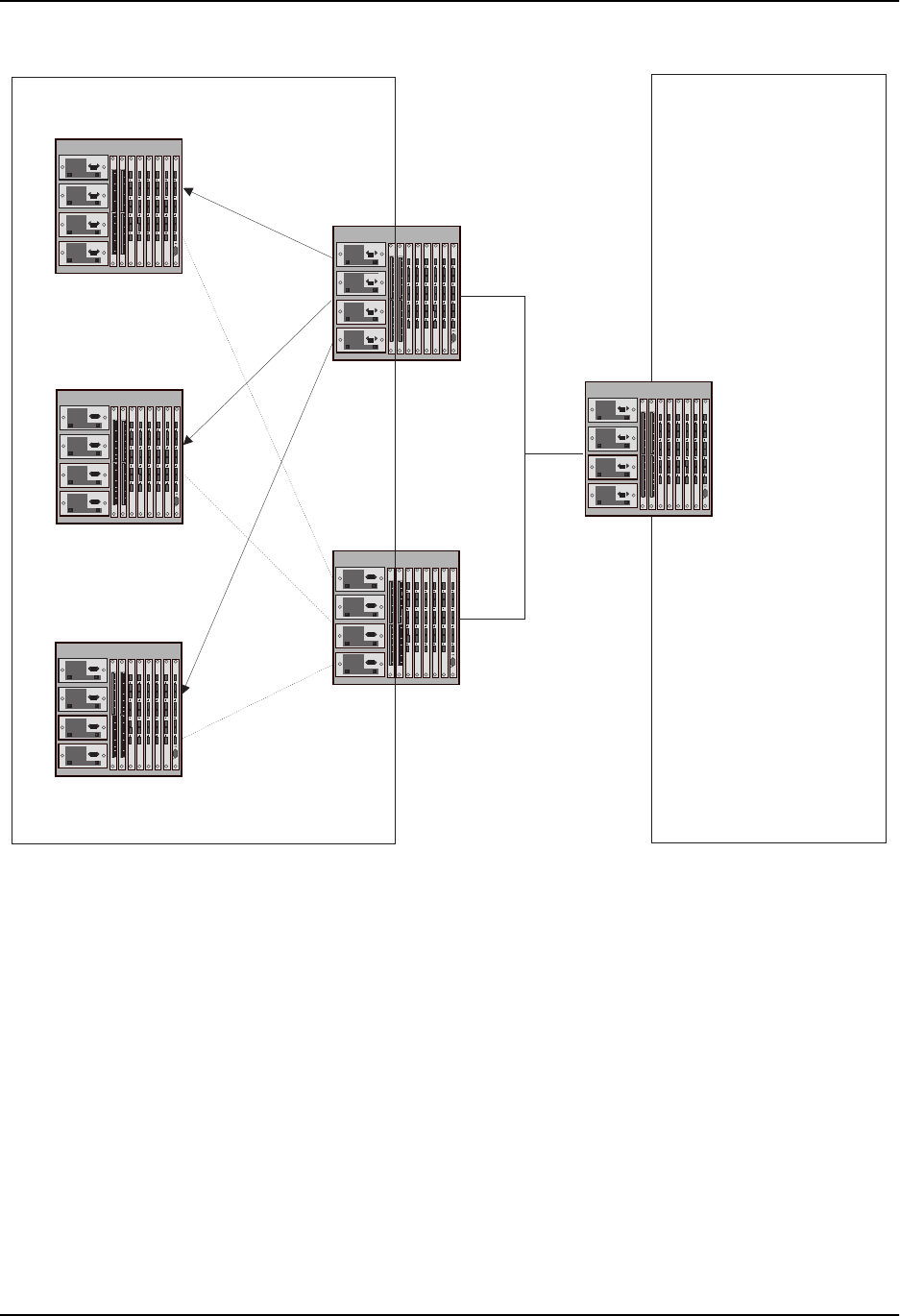
Figure 8.4 AS External LSA reduction
Notice that both Router D and Router E have a route to the other routing domain through Router F. In software
releases earlier than 07.1.X, if Routers D and E have equal-cost routes to Router F, then both Router D and
Router E flood AS External LSAs to Routers A, B, and C advertising the route to Router F. Since both routers are
flooding equivalent routes, Routers A, B, and C receive multiple routes with the same cost to the same destination
(Router F). For Routers A, B, and C, either route to Router F (through Router D or through Router E) is equally
good.
OSPF eliminates the duplicate AS External LSAs. hen two or more HP routing switches configured as ASBRs
have equal-cost routes to the same next-hop router in an external routing domain, the ASBR with the highest
router ID floods the AS External LSAs for the external domain into the OSPF AS, while the other ASBRs flush the
equivalent AS External LSAs from their databases. As a result, the overall volume of route advertisement traffic
within the AS is reduced and the routing switches that flush the duplicate AS External LSAs have more memory
for other OSPF data. n Figure 8.4, since Router D has a higher router ID than Router E, Router D floods the AS
External LSAs for Router F to Routers A, B, and C. Router E flushes the equivalent AS External LSAs from its
database.
Another routing domain
(such as BGP4 or RIP)
Router E
Router ID: 1.1.1.1
OSPF Autonomous System (AS)
Router A
Router F
Router C
Routers D, E, and F
are OSPF ASBRs
and EBGP routers.
Router B
Router D
Router ID: 2.2.2.2
W
I
