Advanced Configuration and Management Guide
• Priority – a parameter used to identify the root bridge in a network. The bridge with the lowest value has the
highest priority and is the root. Possible values: 1 – 65,535. Default is 32,678.
Port Parameters (applied to a specified port within a VLAN)
• Path Cost – a parameter used to assign a higher or lower path cost to a port. Possible values: 1 – 65535.
Default is (1000/Port Speed) for Half-Duplex ports and is (1000/Port Speed)/2 for Full-Duplex ports.
• Priority – value determines when a port will be rerouted in relation to other ports. Possible values: 0 – 255.
Default is 128.
Configuring IP Sub-net, IPX Network and Protocol-Based VLANs
Protocol-based VLANS provide the ability to define separate broadcast domains for several unique Layer 3
protocols within a single Layer 2 broadcast domain. Some applications for this feature might include security
between departments with unique protocol requirements. This feature enables you to limit the amount of
broadcast traffic end-stations, servers, and routers need to accept.
NOTE: See “Configuring AppleTalk Cable VLANs” on page 16-29 for information about configuring an AppleTalk
cable VLAN.
Example: Suppose you want to create four separate Layer 3 broadcast domains within a single Layer 2 STP
broadcast domain:
• Two broadcast domains, one for each of two separate IP sub-nets
• One for IPX Network 1
• One for the Appletalk protocol
Also suppose you want a single router interface to be present within all of these separate broadcast domains,
without using IEEE 802.1p VLAN tagging or any proprietary form of VLAN tagging.
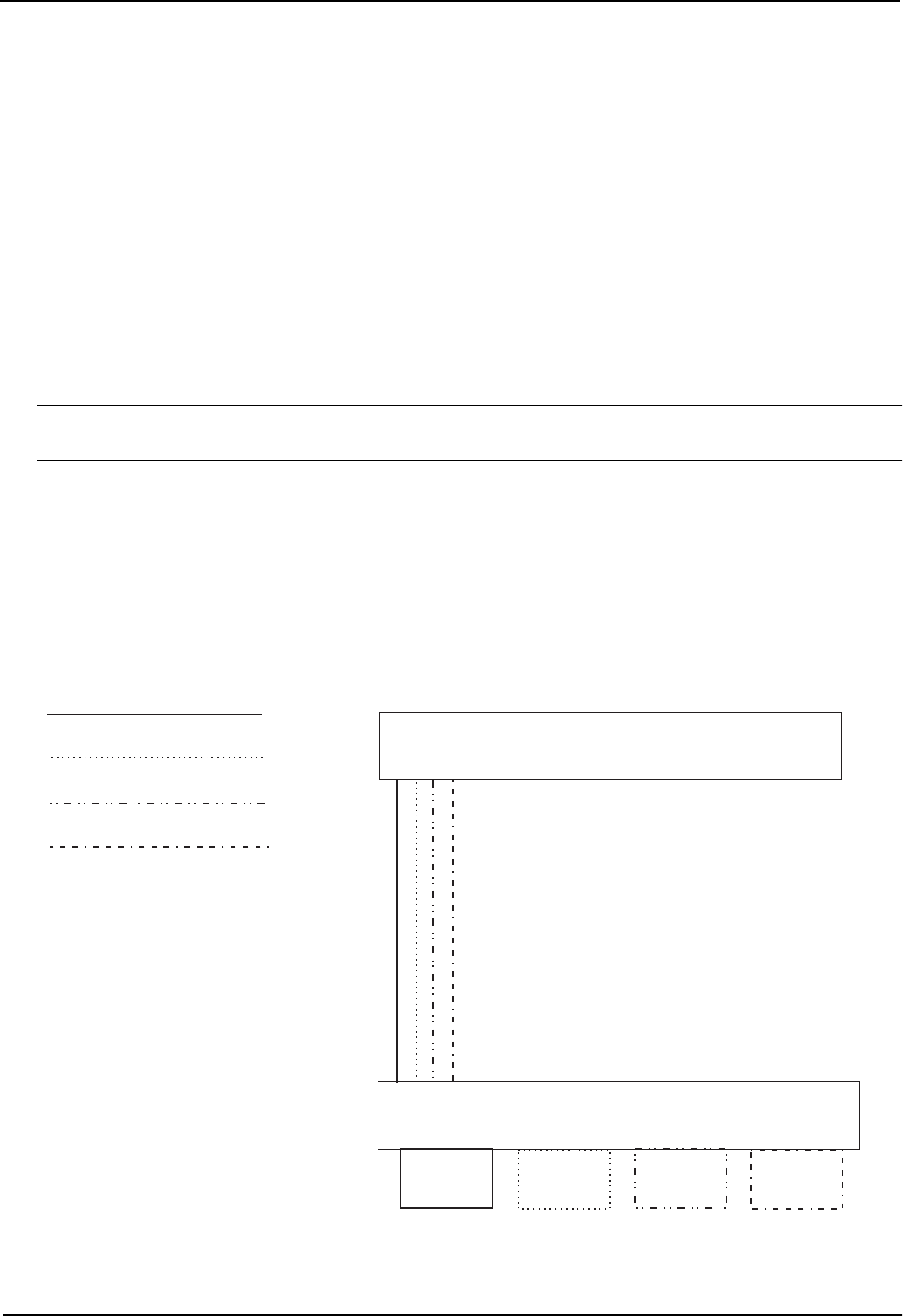
Figure 16.11 shows this configuration.
IP sub-net 1
IP sub-net 2
IPX network 1
AppleTalk cable 100
port 8
Port 8
IP sub-net 1
IPX network 1
AppleTalk cable 100
IP sub-net 2
6208M-SX
6308M-SX
Ports 4 - 6, 8
IP sub-net 2
Ports 1 - 6, 8
IPX network 1
Ports 4 - 6, 8
AppleTalk
cable 100
Ports 1 - 3, 8
IP sub-net 1
Figure 16.11 Protocol-based (Layer 3) VLANs
16 - 20
