Advanced Configuration and Management Guide
10.10.10.3
Port 1/2
209.157.1.1
Outside NAT interface
Internet
10.10.10.2
The device performs NAT
for traffic between the outside
NAT interface and the inside
NAT interface.
NAT Pool = 209.157.1.2 - 254/24
Internet
access router
Port 1/1
10.10.10.1
Inside NAT interface
10.10.10.4
...
10.10.10.254
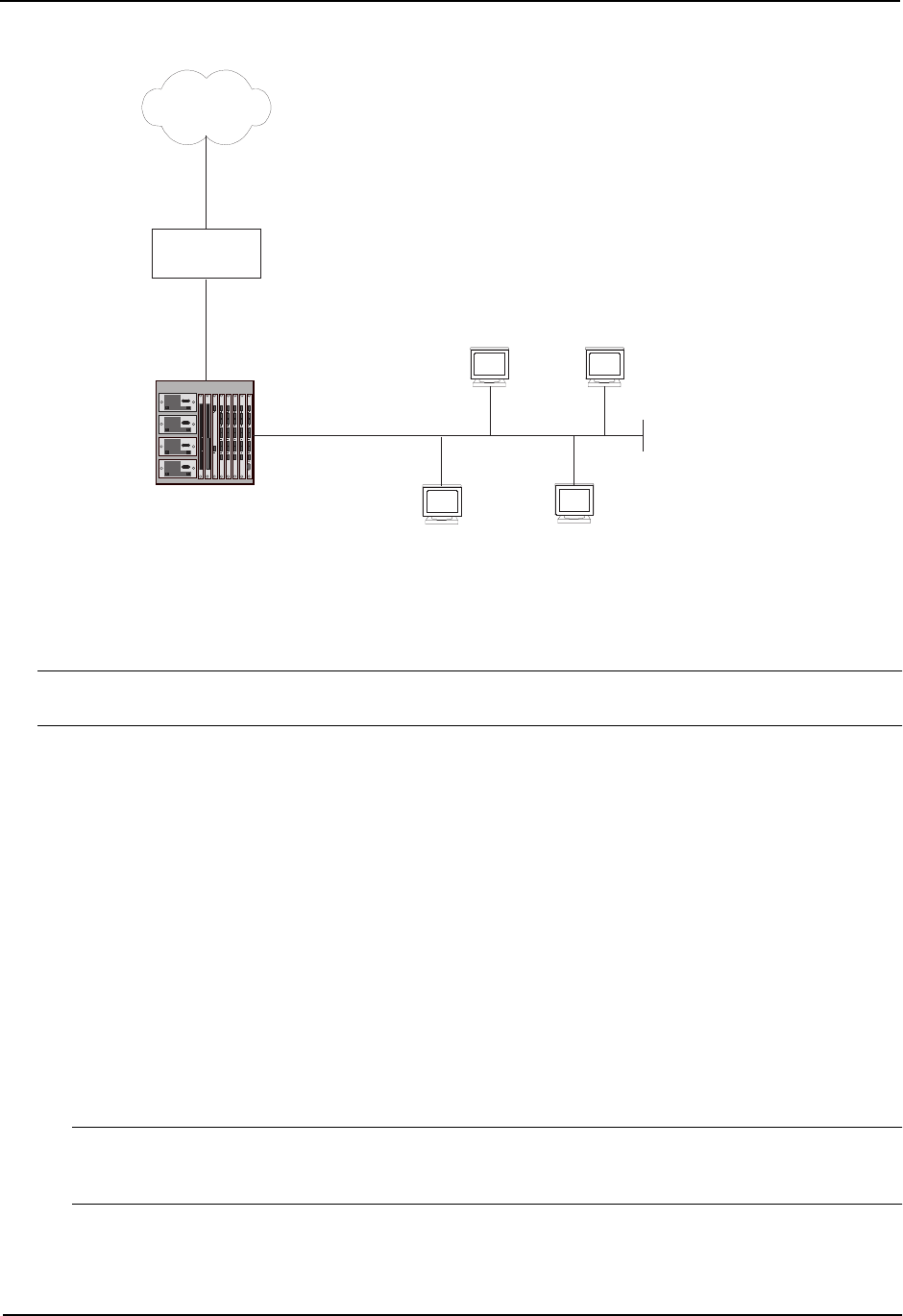
Figure 11.1 Network Using Inside NAT
In this example, the HP 9308M is configured to perform dynamic NAT to translate between the private addresses
in the 10.10.10.x/24 sub-net and the Internet addresses in the 209.157.1.x/24 sub-net.
NOTE: This example is simplified to show how NAT is used. For detailed configuration examples, see
“Configuration Examples” on page 11-14.
To configure NAT on a routing switch, you must configure an inside NAT interface and an outside NAT interface.
• The inside NAT interface is connected to the private addresses.
• The outside NAT interface is connected to the Internet.
The inside NAT interface in Figure 11.1 uses the address pool 209.157.1.2/24 – 209.157.1.254/24 to map the
private addresses to public addresses for traffic initiated by hosts in the 10.10.10.x/24 sub-net.
You can configure the following types of NAT:
• Dynamic NAT – Dynamic NAT maps private addresses to Internet addresses in a pool. The global addresses
come from a pool of addresses that you configure. In the example in Figure 11.1, the pool is the range of
addresses from 209.157.1.2/24 – 209.157.1.254/24. When you use dynamic NAT, the software uses a round
robin technique to select a global IP address to map to a private address from a pool that you configure.
• Static NAT – Static NAT maps a particular global IP address with a particular private address. Use static NAT
when you want to ensure that the software always maps the same global address to a given private address.
For example, use static NAT when you want specific hosts in the private network to always use the same
Internet address when communicating outside the private network.
NOTE: You can configure both dynamic and static NAT on the same HP device. When you configure both
types of NAT, static NAT takes precedence over dynamic NAT. Thus, if you configure a static NAT translation
for a private address, the device always uses that translation instead of creating a dynamic one.
11 - 2
