iDP3221 User’s Manual
133
CITIZEN
13) The printer sets PtrClk back to High. (Event 19)
14) Upon receiving a request for interrupt from the printer, the host responds by setting HostBusy (nAutoFd) to
High. (Event 20)
15) Finally, the printer responds to the host by setting AckDataReq (PError) to Low, and then the host moves to the
Host Busy Data Available phase. (Event 21)
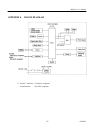
2.4.2 Byte Mode
In this mode, data is transferred between the printer and the host through the procedure described below. The
steps beginning from 1) are applicable when the Negotiation phase has switched to the Host Busy Data Available
phase. If the Negotiation phase has switched to the Host Busy Data Not Available phase, the procedure starts at
step 9).
1) After the negotiations for the entry into the Byte mode are complete, the host indicates that it is ready to
receive data from the printer. This is indicated by switching the data bus to a high-impedance state and setting
HostBusy(nAutoFd)toLow.(Events14and7)
2) The printer places communication data on the data bus. (Event 15)
3) The printer sets PtrClk (nAck) to Low. (Event 9)
4) The host sets HostBusy (nAutoFd) to High to indicate that it has latched data and received the signal in event 9.
(Event 10)
5) The printer must set the four status lines as shown below. (Event 13)
• PtrBusy (Busy): Returned to the status given in the Forward mode.
• nDataAvail (nFault): Set to Low if there is data to be sent.
• AckDataReq (PError): Set to Low if there is data to be sent.
• Xflag (Select): Set to the status given during the last negotiation (i.e., set to Low).
6) The printer sets PtrClk (nAck) to High (event 10) and ends the Byte handshake (event 11).
7) The host indicates that it has succeeded in receiving the data. This is indicated by setting HostClk (nStrobe) to
Low (Event 16) and then to High (Event 17).
8) Events 10 and 16 may occur simultaneously, and events 7 and 17 may occur simultaneously (such as when
HostBusy and HostClk are used together). If this is the case, the host determines the current status by checking:
1. Whether there is more data to be sent from the printer to the host;
2. And whether data can be transferred from the host to the printer.
9) After transferring one byte of data, the printer signals to the host whether it has more data to transfer. When
there is no more data to be received by the host from the printer, the host chooses one of three status selections:
1. Performing Termination and returning to the Compatibility mode.
2. Remaining in the Host Busy Data Not Available phase.
3. Setting HostBusy (nAutoFd) to Low and moving to the Reverse Idle phase (Event 7).