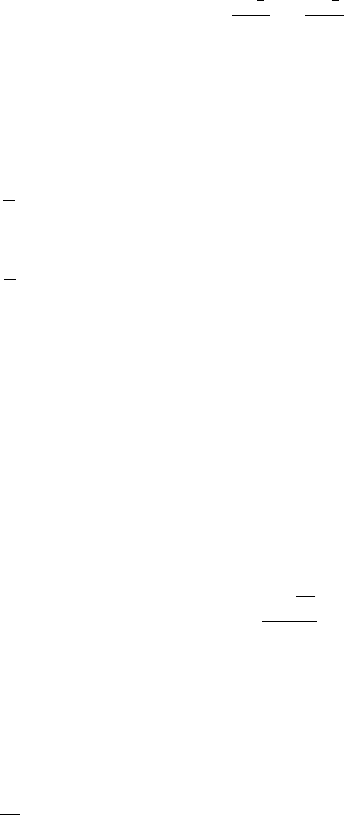
(
)
∑
∑
−=
xy
xyxy
SZA
2
min
Where:
Z
xy
= Amplitude of the pixel data at (x,y).
S
xy
= Amplitude of fitted surface at (x,y).
6.14 Whole Beam fit equations
The bivariate normal equation is used to fit data in two locked directions, X and Y. The Whole Beam
selection assumes the beam is round or elongated parallel to the horizontal or vertical axis. The
definition of the bivariate normal equation and the displayed results are as follows:
−
+
−
−
=
2
2
2/2/
2
y
w
yy
x
w
xx
eJJ
o
Where:
J
= Amplitude at the point (
x,y
).
J
o
* = Amplitude at the Gaussian center.
x
=
x
location of pixel.
x
* =
x
location of the Gaussian center.
w
x
* = Horizontal width at 1/e² of energy.
y
=
y
location of pixel.
y
* =
y
location of the Gaussian center.
w
y
* = Vertical width at 1/e² of energy.
Parameters marked with an asterisk (*) are the variables fitted.
6.15 X/Y or Major/Minor line fit equations
The univariate normal equation is used to fit data in one direction. The definition of the equation and
the displayed results are shown below:
for the X or Major axis
2
2/
2
−
−
=
M
w
MM
M
eJJ
Where:
J
= Amplitude at the point
M
.
J
M
*
= Amplitude at the Gaussian center.
M
= Location of pixel.
M
= location of the Gaussian center.
w
M
* = Width at 1/e² of energy.
Operator’s Manual LBA-PC
136


















