Instruction Manual
748467-A
January 2002
1-6 Description and Specifications Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management
Model MicroCEM
b. Paramagnetic Oxygen Method
The paramagnetic principle refers to the
induction of a weak magnetic field, paral-
lel and proportional to the intensity of a
stronger magnetizing field.
The paramagnetic method of determina-
tion of oxygen concentration utilizes nitro-
gen filled quartz spheres arranged at
opposite ends of a bar, the center of
which is suspended by and free to rotate
on a thin platinum wire ribbon in a cell.
Nitrogen (N
2
) is used because it is dia-
magnetic or repelled by a magnet.
A small mirror that reflects a light beam
coming from a light source to a photode-
tector, is mounted on the platinum ribbon.
A strong permanent magnet specifically
shaped to produce a strong, highly inho-
mogeneous magnetic field inside the
analysis cell, is mounted outside the wall
of the cell.
When oxygen molecules enter the cell,
their paramagnetism will cause them to
be drawn towards the region of greatest
magnetic field strength. The oxygen
molecules thus exert different forces on
the two suspended nitrogen filled quartz
spheres, producing a torque which
causes the mirror to rotate away from its
equilibrium position.
The rotated mirror deflects the incident
light onto the photodetector creating an
electrical signal which is amplified and fed
back to a coil attached to the bar holding
the quartz spheres, forcing the suspended
spheres back to the equilibrium position.
The current required to generate the re-
storing torque to return the quartz bar to
its equilibrium position is a direct measure
of the O
2
concentration in the sample gas.
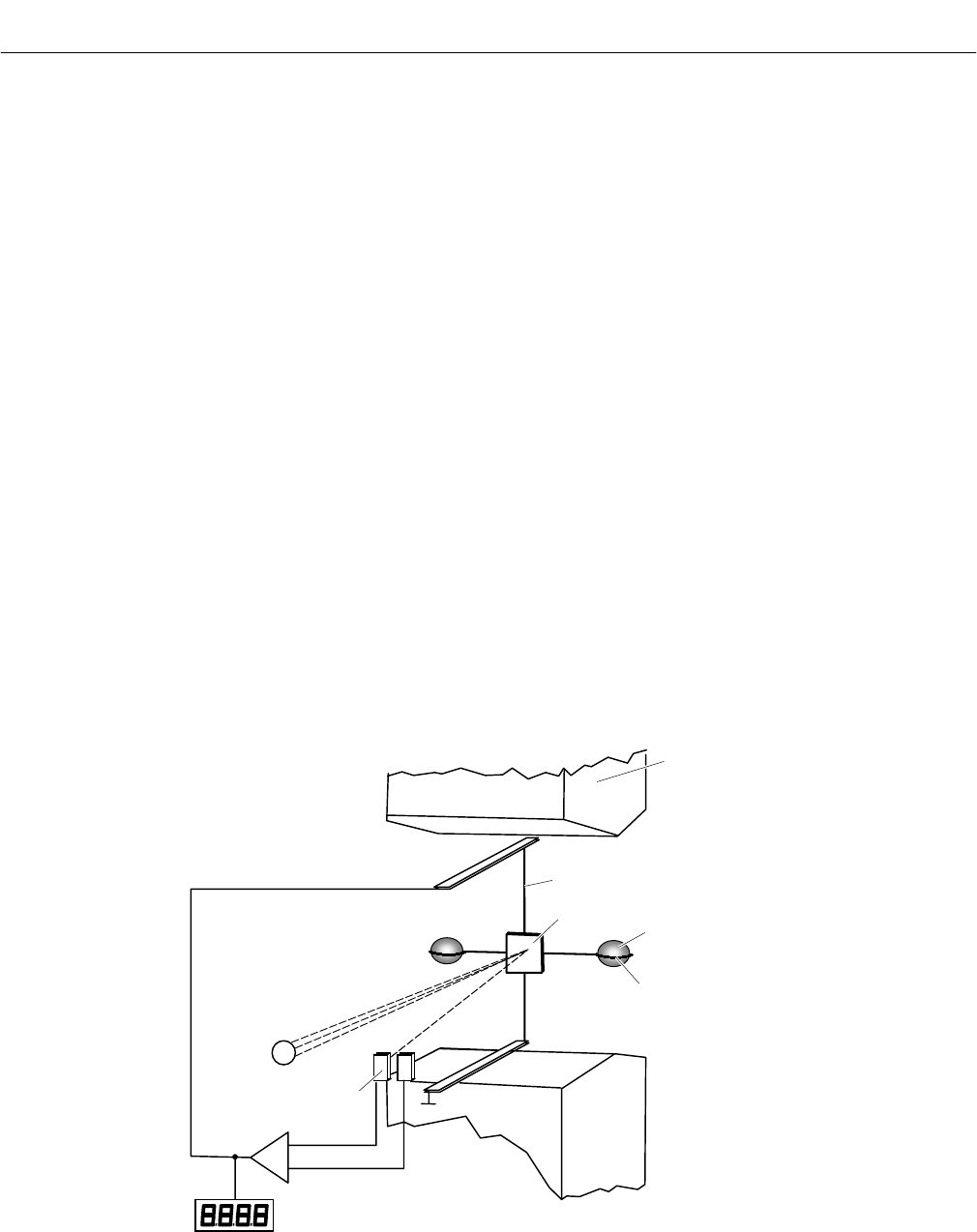
The complete paramagnetic analysis cell
consists of an analysis chamber, perma-
nent magnet, processing electronics, and
a temperature sensor. The temperature
sensor is used to control a heat ex-
changer to warm the measuring gas to
about 55 °C. Refer to Figure 1-4.
Figure 1-4. Paramagnetic Oxygen Analysis
Permanent Magnet
Platinum Wire
Mirror
Quartz Sphere(s)
Photodetector
Light
Source
Wire Loop
Amplifier
Display