Instruction Manual
748467-A
January 2002
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Description and Specifications 1-7
Model MicroCEM
c. Electrochemical Oxygen Method
The electrochemical method of determin-
ing oxygen concentration is based on the
galvanic cell principle shown in Figure
1-5.
The electrochemical oxygen sensor (Fig-
ure 1-6) incorporates a lead and gold gal-
vanic process with a lead anode and a
gold cathode, using an acid electrolyte.
Oxygen molecules diffuse through a non-
porous Teflon membrane into the electro-
chemical cell and are reduced at the gold
cathode. Water is the byproduct of this
reaction.
On the anode, lead oxide is formed which
is transferred into the electrolyte. The lead
anode is continuously regenerated and,
therefore, the electrode potential remains
unchanged for a long time. The rate of
diffusion and corresponding response
time (t90) of the sensor is dependent on
the thickness of the Teflon membrane.
The electric current between the elec-
trodes is proportional to the O
2
concentra-
tion in the sample gas being measured.
The resultant signal is measured as a
voltage across the resistor and thermistor,
the latter of which is used for temperature
compensation. A change in the output
voltage (mV) represents oxygen concen-
tration.
NOTE
The electrochemical O
2
cell requires a
minimum internal consumption of
oxygen. Sample gases with an oxygen
concentration of less than 2% could
result in a reversible detuning of sensi-
tivity and the output will become un-
stable. The recommended practice is
to purge the cell with conditioned am-
bient air between periods of measure-
ment. If the oxygen concentration is
below 2% for several hours or days,
the cell must be regenerated for about
one day with ambient air. Temporary
flushing with nitrogen (N
2
) for less than
one hour (analyzer zeroing) will have
no effect on the sensitivity or stability.
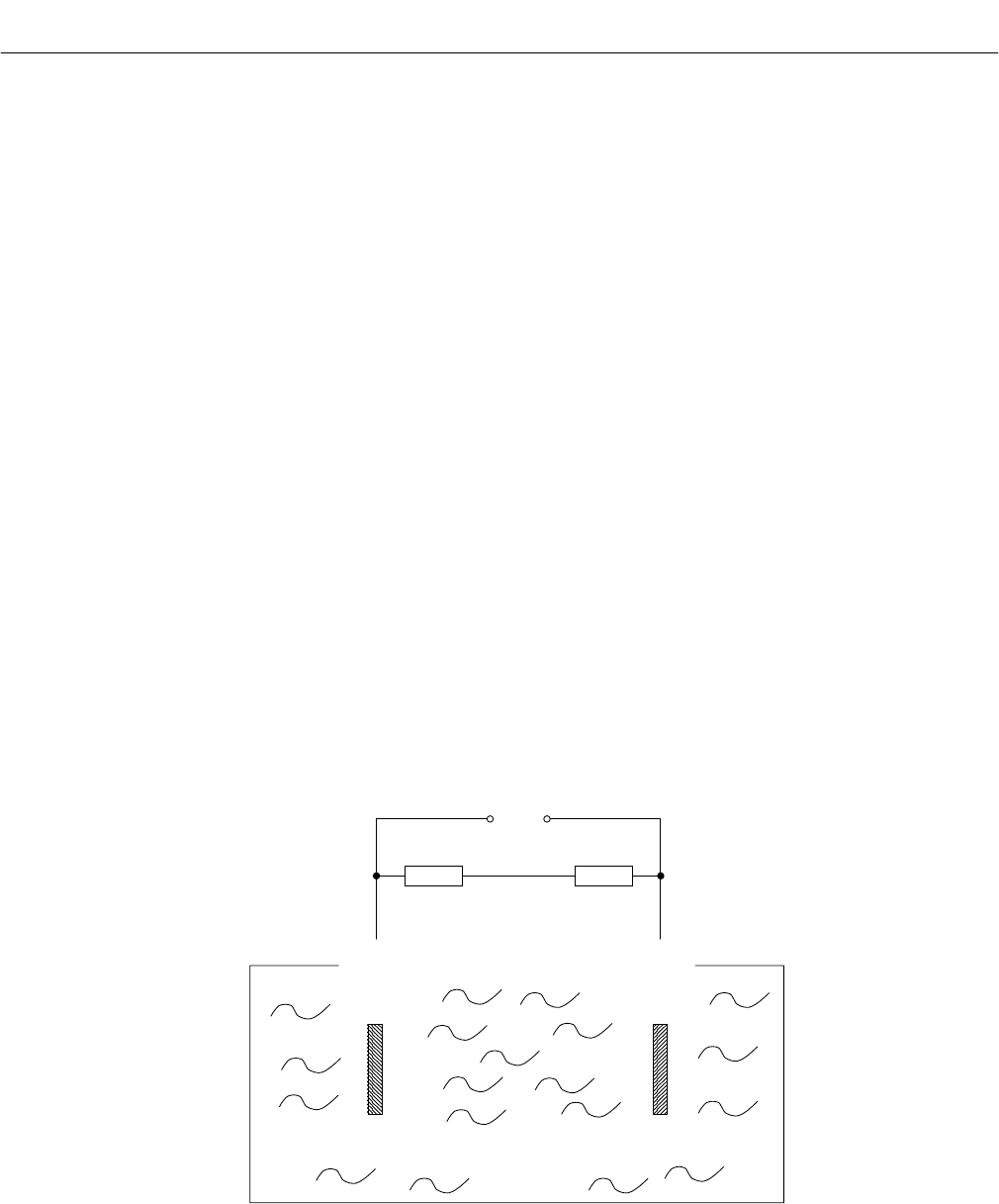
Figure 1-5. Reaction of Galvanic Cell
(Red) V out (Black)
Thermistor (5) Resistor (6)
(-) (+)
Gold Lead
Cathode (2) Anode (1)
O
2
+ 4 H + 4 e
→
2 H
2
O2 Pb + 2 H
2
O
→
2PbO + 4 H + 4 e
Electrolyte (3)
(ph 6)
Summary reaction O
2
+ 2 Pb
→
2 PbO