Chapter 5 Operation 61
61
The readout time is approximately given by:
(2)
where
N
x
is the smaller dimension of the CCD
N
y
is the larger dimension of the CCD
t
sr
is the time needed to shift one pixel out of the shift register
t
v
is the time needed to digitize a pixel
t
i
is the time needed to shift one line into the shift register
A subsection of the CCD can be read out at full resolution, sometimes dramatically
increasing the readout rate while retaining the highest resolution in the region of interest
(ROI). To approximate the readout rate of an ROI, in Equation 2 substitute the x and y
dimensions of the ROI in place of the dimensions of the full CCD. Some overhead time,
however, is required to read out and discard the unwanted pixels.
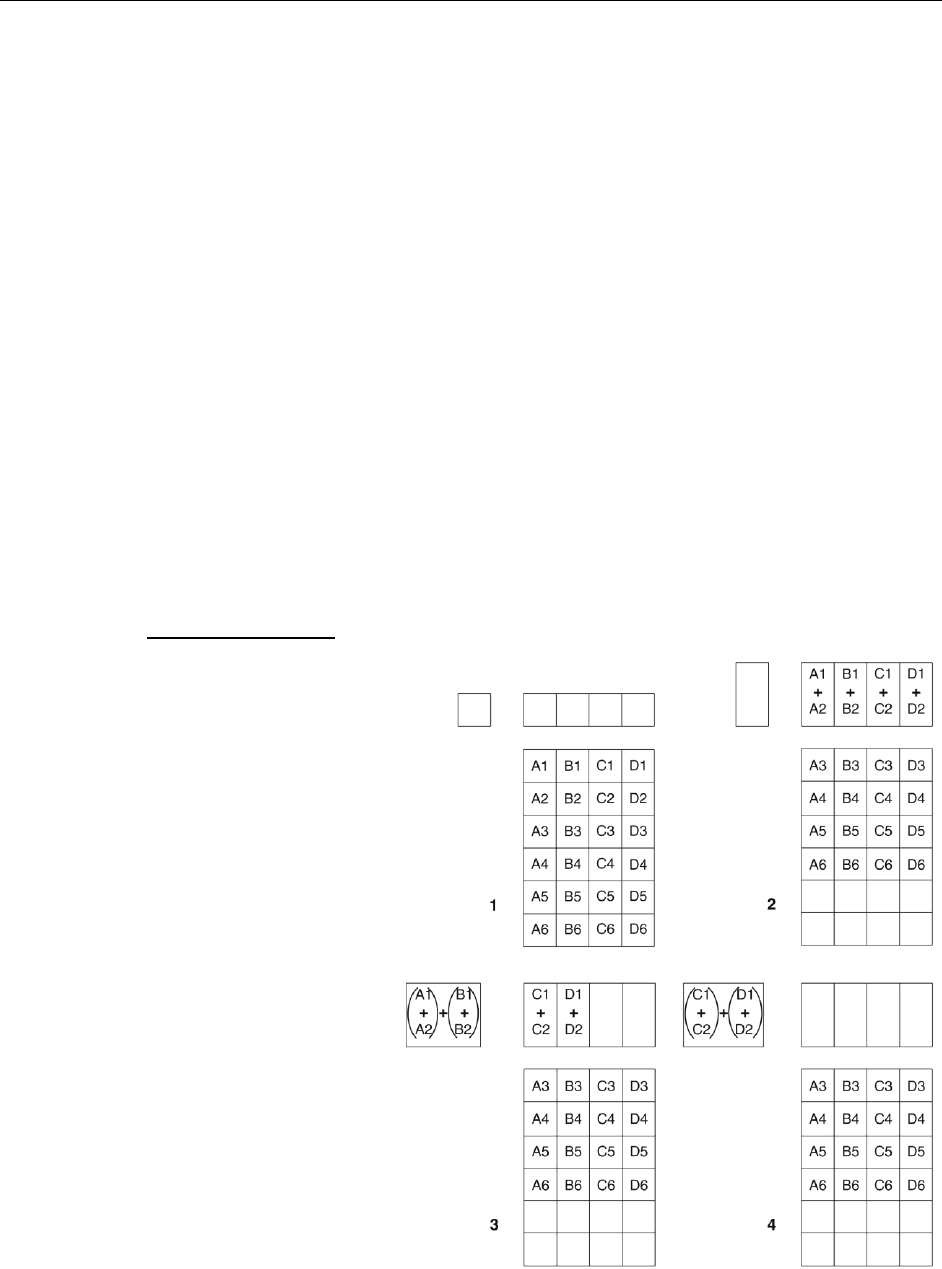
Binning
Binning is the process of adding the data from adjacent pixels together to form a single
pixel (sometimes called a super pixel), and it can be accomplished in either hardware or
software. Rectangular groups of pixels of any size may be binned together, subject to
some hardware and software limitations.
Hardware Binning
Hardware binning is
performed on the CCD
array before the signal is
read out of the output
amplifier. For signal levels
that are readout noise
limited this method
improves S/N ratio linearly
with the number of pixels
grouped together. For
signals large enough to
render the camera photon
shot noise limited, the S/N
ratio improvement is
roughly proportional to the
square-root of the number
of pixels binned.
Binning also reduces
readout time and the
burden on computer
memory, but at the
expense of resolution.
Since shift register pixels
typically hold only twice
as much charge as image
Figure 26. 2 × 2 Binning
i
x
v
sr
y
x
R
t
N
t
t
N
N
t


















