52
D14049.03
MAY 2008
Grey Headline (continued)
About the DNS Domain Name
The DNS Domain Name is used when attempting to resolve
server addresses congured on the VCS that are without
any form of qualication (e.g. ldap or ldap_server but not
ldap.server). It applies only to the following:
LDAP server
•
NTP server
•
External Manager server.
•
The DNS Domain Name is appended to the unqualied server
address before a query to the DNS server is executed.
If the server address is an IP address or is in the format of a
domain name, DNS will only be queried for the server address
as congured, without the DNS Domain Name appended. For
this reason we recommend that all server addresses use an IP
address or FQDN (Fully Qualied Domain Name).
The DNS Domain name plays no part in URI dialing.
Save
Click here to save your
changes.
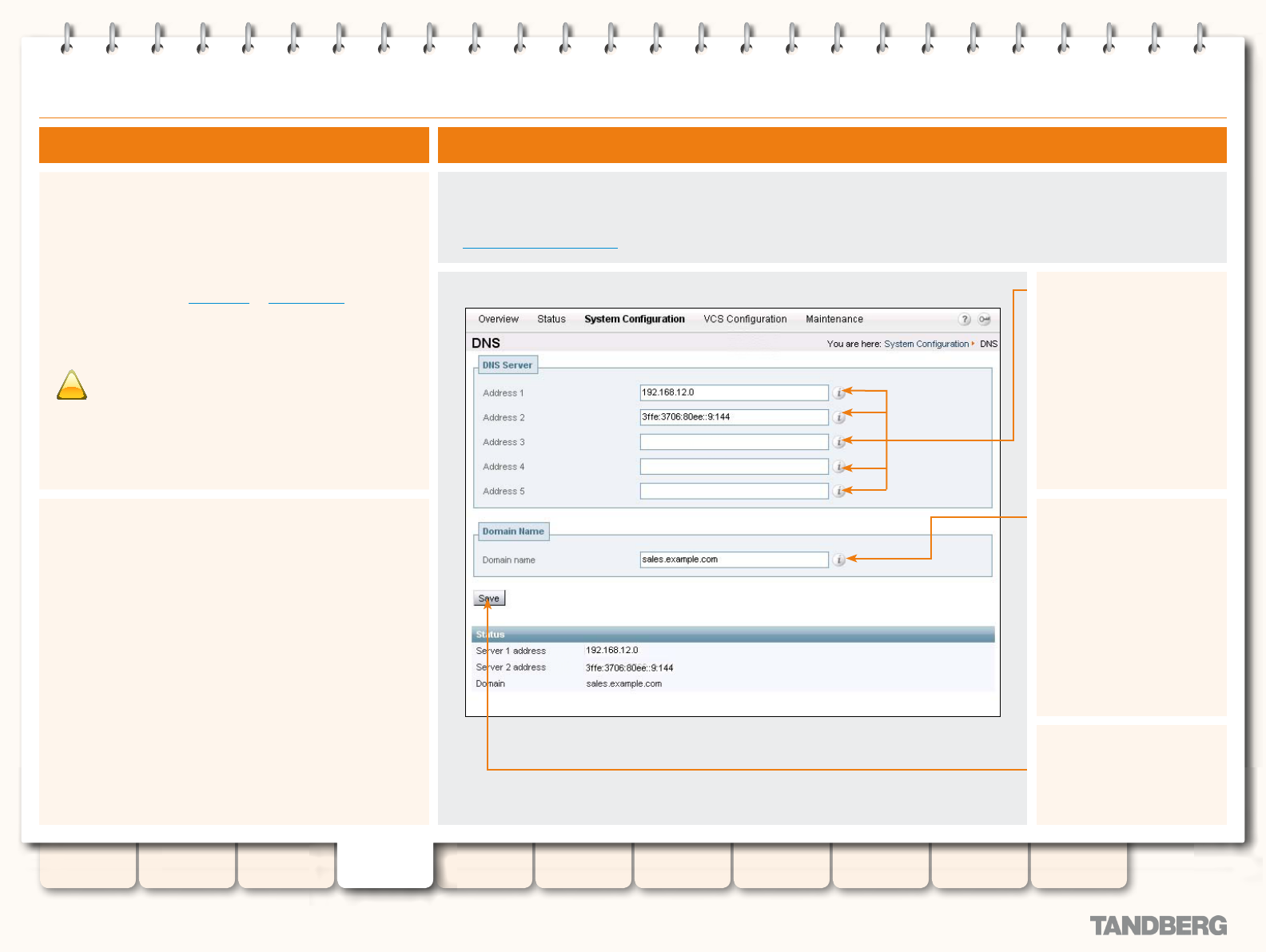
To congure the VCS’s DNS settings:
System Conguration > DNS
•
.
You will be taken to the DNS page.
xConguration IP DN
•
S
Address 1 to Address 5
Sets the IP address of a DNS
server to be queried when
resolving domain names.
Domain name
Species the name to be
appended to an unqualied
server address before a
query to the DNS server is
executed.
Conguration
Overview
About DNS Servers
You must specify at least one DNS server to be queried for
address resolution if you wish to either:
use FQDNs (Fully Qualied Domain Names) instead of IP
•
addresses when specifying external addresses (for example
for LDAP and NTP servers, neighbor zones and alternates), or
use features such as
•
URI dialing or ENUM dialing,
You can specify up to 5 DNS servers. The VCS sends requests
to all congured servers in parallel taking the rst result
received and discounting the rest.
!
This can lead to confusing behavior should local network
administrators, for example, deploy ‘split horizon’ DNS
where records held on an internal, corporate, DNS
server use the same domain names but with different values to
those on the public internet - an often used tactic in corporate
intranets.
TANDBERG VIDEO COMMUNICATIONS SERVER
ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Introduction Getting Started
Overview and
Status
System
Conguration
VCS
Conguration
Zones and
Neighbors
Call
Processing
Bandwidth
Control
Firewall
Traversal
Maintenance Appendices
DNS


















