D 14049.01
07.2007
40
TANDBERG VIDEO COMMUNICATION SERVER
ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Text goes here
Introduction
Getting
Started
System
Overview
System
Configuration
H.323 & SIP
Configuration
Registration
Control
Zones and
Neighbors
Call
Processing
Firewall
Traversal
Bandwidth
Control
Maintenance
Appendices
TANDBERG VIDEO COMMUNICATION SERVER
ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Registration
Control
Registration Control
Registration Overview
Finding a VCS with which to Register
Before an endpoint can register with a VCS, it must determine which VCS it can or should be
registering with. This setting is configured on the endpoint, and the process is different for SIP
and H.323.
SIP
SIP endpoints must find a SIP Registrar with which to register. The SIP Registrar maintains a
record of the endpoint’s details against the endpoint’s Address of Record (AOR). When a call is
received for that AOR, the SIP Registrar refers to the record in order to find the endpoint to which
it corresponds. (Note that the same AOR can be used by more than one SIP endpoint at the same
time.)
The SIP Registrar will only accept registrations for domains for which it is authoritative.
There are two ways a SIP endpoint can locate a Registrar with which to register: manually or
automatically. The option is configured on the endpoint itself under the SIP Server Discovery
option (consult your endpoint user guide for how to access this setting).
If the mode is set to automatic, the endpoint will send a REGISTER message to its SIP
Server. This will be forwarded (via DNS if necessary) to the Registrar that is authoritative for
the domain with which the endpoint is attempting to register. For example, if an endpoint is
attempting to register with a URI of john.smith@example.com, the request will be sent to the
Registrar authoritative for the domain example.com.
If the mode is set to manual, the user must specify the IP address of the Registrar with which
they wish to register, and the endpoint will attempt to register with that Registrar only.
The VCS is a SIP Server for endpoints in its local zone, and can also act as a SIP Registrar.
If the VCS is acting as the endpoint’s SIP Server and SIP Registrar, when the registration
request is received from the endpoint it will be accepted by the VCS and the endpoint will be
registered and able to receive inbound calls. See Using the VCS as a SIP Registrar for more
information.
If the VCS is acting as the endpoint’s SIP server but is not a SIP Registrar, it will proxy the
registration request. See Proxying registration requests for more information.
•
•
•
•
H.323
There are two ways an H.323 endpoint can locate a VCS with which to register: manually or
automatically. The option is configured on the endpoint itself under the Gatekeeper Discovery
setting (consult your endpoint manual for how to access this setting).
If the mode is set to automatic, the endpoint will try to register with any VCS it can find. It does
this by sending out a Gatekeeper Discovery Request, to which eligible VCSs will respond.
If the mode is set to manual, you must specify the IP address of the VCS with which you wish
your endpoint to register, and the endpoint will attempt to register with that VCS only.
•
•
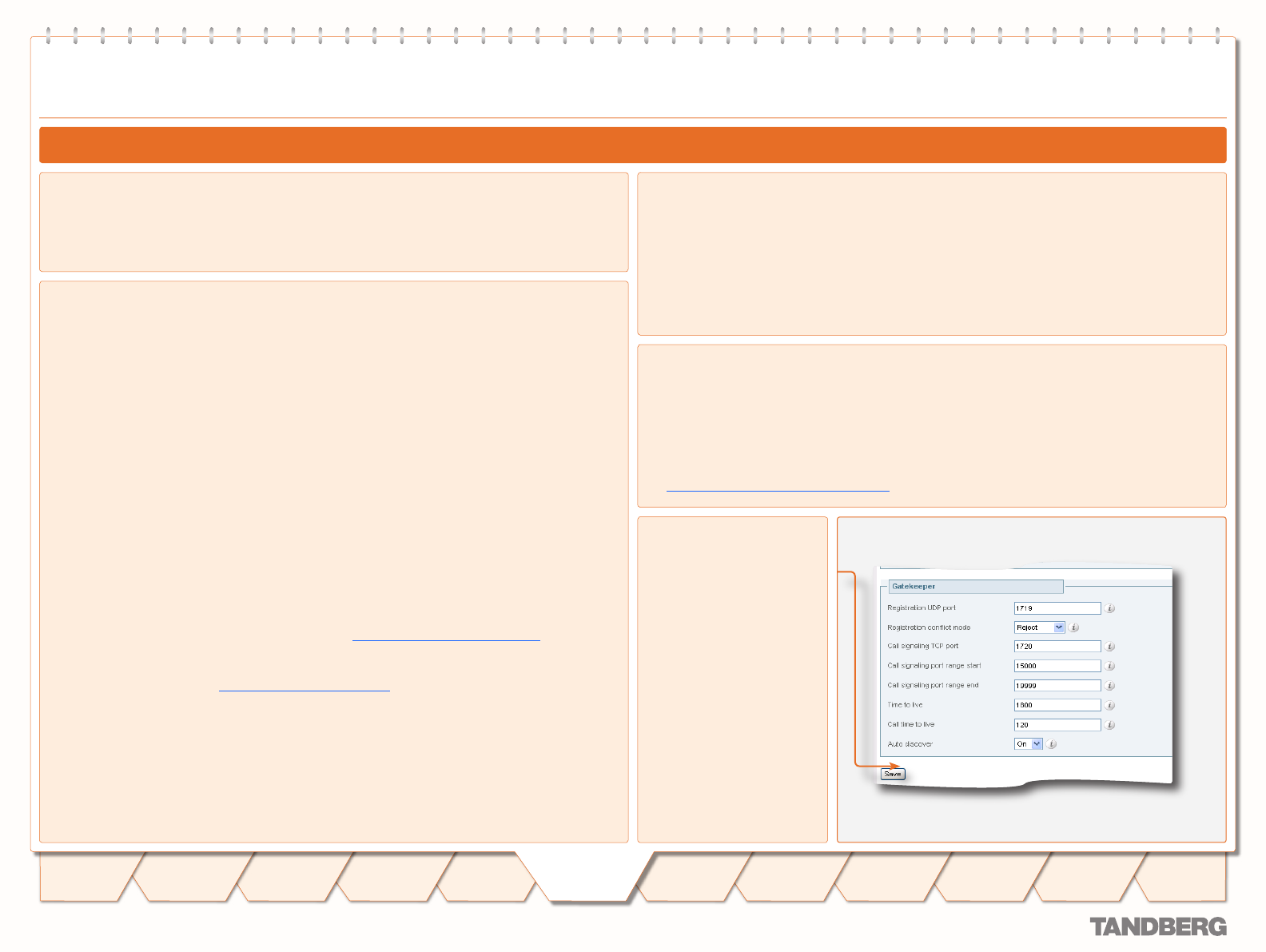
Auto discover
On: The VCS will respond
to Gatekeeper discovery
requests.
Off: The VCS will not
respond to Gatekeeper
discovery requests. H.323
endpoints will be able to
register with the VCS only if
their Gatekeeper Discovery
setting is Manual and they
have entered the IP address
of the VCS.
Preventing automatic registrations
You can prevent H.323 endpoints being able to register automatically with the VCS by disabling
Auto Discovery on the VCS. The Auto Discovery setting determines whether the VCS responds to
the Gatekeeper Discovery requests sent out by endpoints.
To configure the Auto Discovery setting:
VCS Configuration > Protocols > H.323.
You will be taken to the H.323 page.
H323 Gatekeeper AutoDiscovery
•
•