D 14049.01
07.2007
55
D 14049.01
07.2007
55
Introduction
Getting
Started
System
Overview
System
Configuration
H.323 & SIP
Configuration
Registration
Control
Zones and
Neighbors
Call
Processing
Firewall
Traversal
Bandwidth
Control
Maintenance
Appendices
Zones and
Neighbors
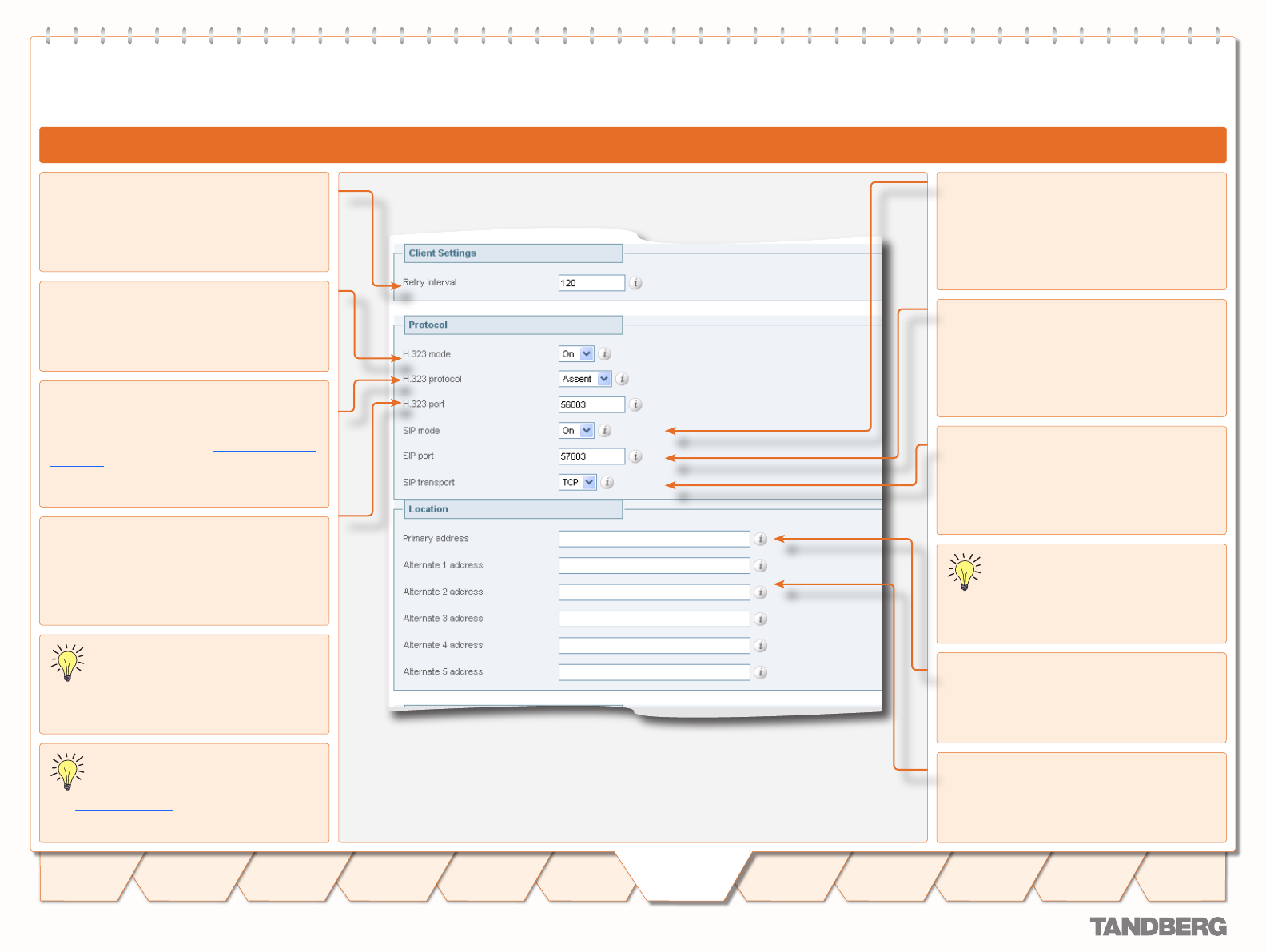
Configuring Traversal Client Zones
H.323 protocol
Determines which of the two firewall traversal
protocols (Assent or H.460.18) to use for calls
to the traversal server. (See Firewall Traversal
Protocols for more information.)
H.323 port
Specifies the port on the traversal server to
be used for H.323 calls to and from the local
VCS.
SIP transport
Determines which transport type will be used
for SIP calls to and from the traversal server.
SIP port
Specifies the port on the traversal server to
be used for SIP calls to and from the VCS.
Retry interval
Specifies the interval in seconds with which a
failed attempt to establish a connection to the
traversal server should be retried.
Primary address
Specifies the IP address or FQDN of the
traversal server.
Alternate 1 to Alternate 5 address
Specifies the IP addresses or FQDNs of any
alternates configured on the traversal server.
H.323 mode
Determines whether H.323 calls will be
allowed to and from the traversal server.
SIP mode
Determines whether SIP calls will be allowed
to and from this zone.
For firewall traversal to work via
H.323, the traversal server must have
a traversal server zone configured on it
to represent this VCS, using this same port
number.
For firewall traversal to work via SIP,
the traversal server must have a
traversal server zone configured on it
to represent this VCS, using this same
transport type and port number.
For full details on how traversal client
zones and traversal server zones work
together to achieve firewall traversal,
see Firewall Traversal.
TANDBERG VIDEO COMMUNICATION SERVER
ADMINISTRATOR GUIDE
Managing Zones, Neighbors and Alternates