Chapter 6 File Operations
100
6-3 FTP File Operations
6-3-1 Command List
This unit supports standard FTP commands (see the next
section), and extended FTP commands (see page 104).
Standard commands
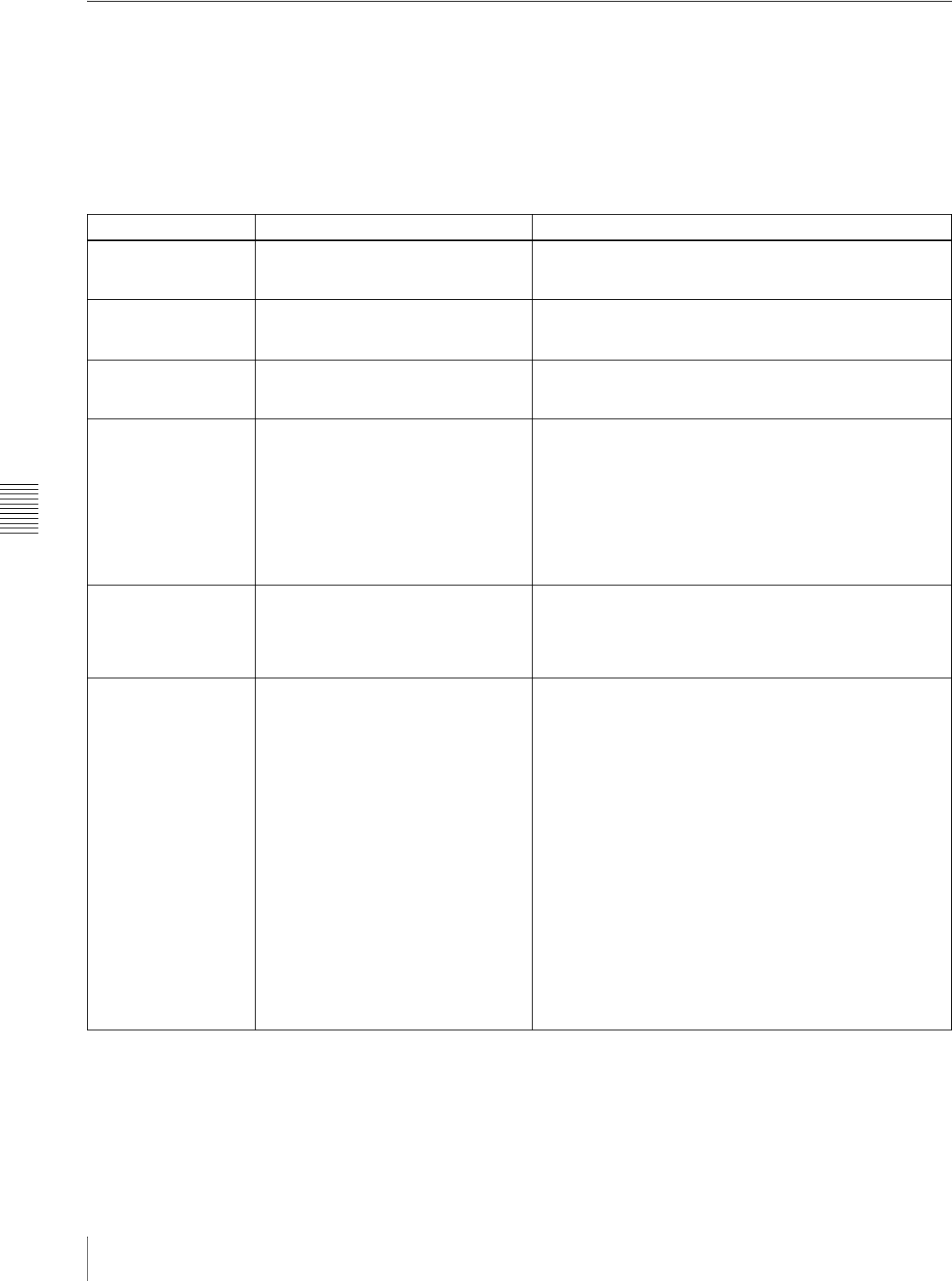
The following table shows the standard FTP commands
supported by this unit.
In the command syntax column, <SP> means a space,
entered by pressing the space bar, and <CRLF> means a
new line, entered by pressing the Enter key.
Command name Description Command syntax
USER Send this command to begin the login
process.
USER <SP> <username> <CRLF>
Input example: USER admin
PASS After sending the USER command,
send this command to complete the
login process.
PASS <SP> <password> <CRLF>
Input example: PASS pdw-530 (or 510)
QUIT Terminates the FTP connection. If a file
is being transferred, terminates after
completion of the transfer.
QUIT <CRLF>
PORT Specifies the IP address and port to
which this unit should connect for the
next file transfer (for data transfer from
this unit).
PORT <SP> <h1,h2,h3,h4,p1,p2> <CRLF>
• h1 (most significant byte) to h4 (least significant byte): IP
address
• p1 (most significant byte), p2 (least significant byte): Port
address
Input example: PORT 10,0,0,1,242,48
(IP address: 10.0.0.1, Port number: 62000)
PASV This command requests this unit to
“listen” on a data port (which is not its
default data port). It puts this unit into
passive mode, waiting for the remote
computer to make a data connection.
PASV <CRLF>
TYPE Specifies the type of data to be
transferred.
TYPE <SP> <type-code (options delimited by <SP>)>
<CRLF>
<type-code> can be any of the following. However, for
XDCAM, data is always transferred as “I,” regardless of the
type-code specification.
• A: ASCII
- N: Non-print (default)
- T: Telnet format
- C: ASA Carriage Control
• E: EBCDIC
-N: Non-print
- T: Telnet format
- C: ASA Carriage Control
• I: IMAGE (Binary)
• L: LOCAL BYTE
- SIZE: byte size
Input example: TYPE I


















