9-7
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual, R7.2
Chapter 9 Management Network Connectivity
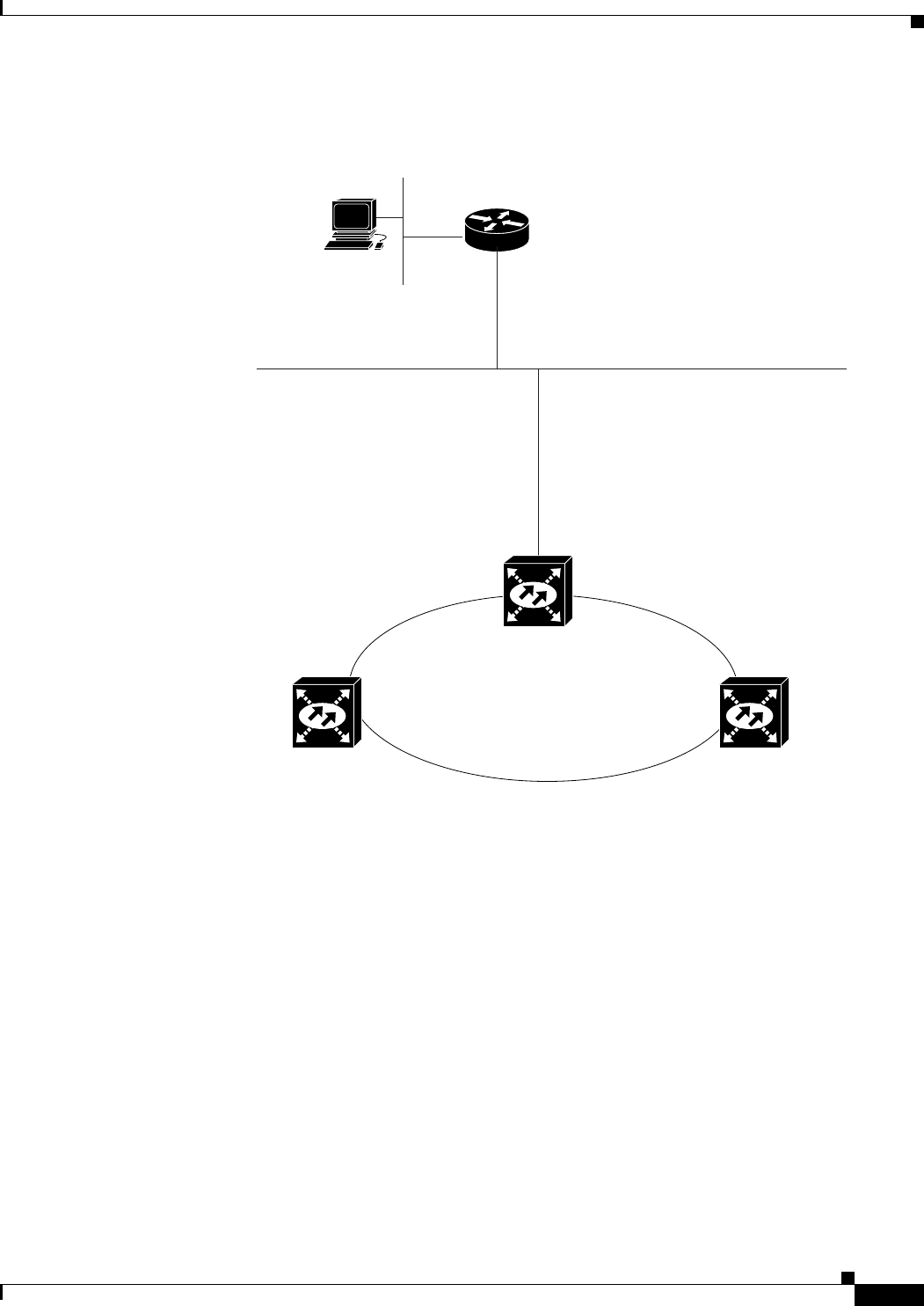
9.2.5 Scenario 5: Using Static Routes to Connect to LANs
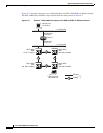
Figure 9-5 Scenario 5: Static Route with One CTC Computer Used as a Destination
The destination and subnet mask entries control access to the ONS 15600s:
•
If a single CTC computer will be connected to a router, enter the complete CTC “host route” IP
address as the destination with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255.
•
If CTC computers on a subnet are connected to a router, enter the destination subnet (in this
example, 192.168.1.0) and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
•
If all CTC computers are connected to router, enter a destination of 0.0.0.0 and a subnet mask of
0.0.0.0. Figure 9-6 shows an example.
In this figure, the IP address of router interface B is entered as the next hop (the next router that a packet
traverses to reach its destination), and the cost (number of hops from source to destination) is 2.
CTC Workstation
IP Address 192.168.1.100
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway = 192.168.1.1
Host Routes = N/A
Router
IP Address of interface ”A” to LAN “A” 192.168.1.1
IP Address of interface “B” to LAN “B” 192.168.2.1
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
ONS 15600 #2
IP Address 192.168.3.20
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Router = N/A
Static Routes = N/A
ONS 15600 #1
IP Address 192.168.2.10
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Router = 192.168.2.1
Static Routes
Destination 192.168.1.0
Mask 255.255.255.0
Next Hop 192.168.2.1
Cost = 2
ONS 15600 #3
IP Address 192.168.4.30
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Router = N/A
Static Routes = N/A
LAN B
LAN A
Int "A"
Int "B"
SONET RING
81205