9-32
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual, R7.2
Chapter 9 Management Network Connectivity
9.7.4 OSI Routing
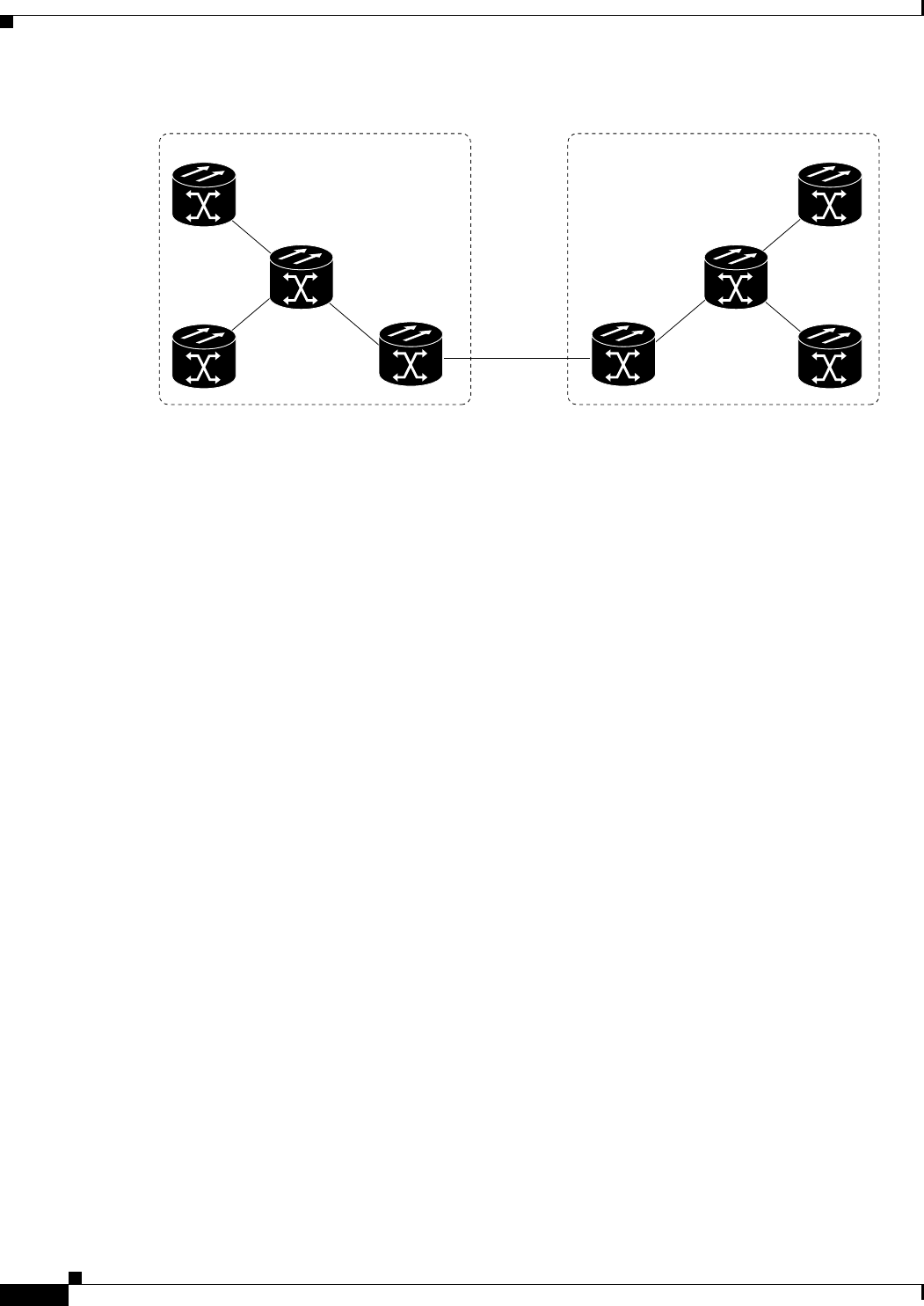
Figure 9-21 Level 1 and Level 2 OSI Routing
When you provision an ONS 15600 for a network with NEs that use both the TCP/IP and OSI protocol
stacks, you will provision it as one of the following:
•
Intermediate System Level 1—The ONS 15600 performs OSI IS functions. It communicates with
IS and ES nodes that reside within its OSI area. It depends upon an IS L1/L2 node to communicate
with IS and ES nodes that reside outside its OSI area.
•
Intermediate System Level 1/Level 2—The ONS 15600 performs IS functions. It communicates
with IS and ES nodes that reside within its OSI area. It also communicates with IS L1/L2 nodes that
reside in other OSI areas. This option should not be provisioned unless the node is connected to
another IS L1/L2 node that resides in a different OSI area. The node must also be connected to all
nodes within its area that are provisioned as IS L1/L2.
9.7.4.1 End System-to-Intermediate System Protocol
ES-IS is an OSI protocol that defines how ESs (hosts) and ISs (routers) learn about each other. ES-IS
configuration information is transmitted at regular intervals through the ES and IS hello messages. The
hello messages contain the subnetwork and network layer addresses of the systems that generate them.
The ES-IS configuration protocol communicates both OSI network layer addresses and OSI subnetwork
addresses. OSI network layer addresses identify either the NSAP, which is the interface between OSI
Layer 3 and Layer 4, or the NET, which is the network layer entity in an OSI IS. OSI SNPAs are the
points at which an ES or IS is physically attached to a subnetwork. The SNPA address uniquely identifies
each system attached to the subnetwork. In an Ethernet network, for example, the SNPA is the 48-bit
MAC address. Part of the configuration information transmitted by ES-IS is the NSAP-to-SNPA or
NET-to-SNPA mapping.
9.7.4.2 Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System
IS-IS is an OSI link-state hierarchical routing protocol that floods the network with link-state
information to build a complete, consistent picture of a network topology. IS-IS distinguishes between
Level 1 and Level 2 ISs. Level 1 ISs communicate with other Level 1 ISs in the same area. Level 2 ISs
route between Level 1 areas and form an intradomain routing backbone. Level 1 ISs need to know only
how to get to the nearest Level 2 IS. The backbone routing protocol can change without impacting the
intra-area routing protocol.
Level 2
routing
Area 1
IS IS
IS IS
Area 2
Domain
Level 1
routing
Level 1
routing
ES
131597
ES
ES
ES