8-5
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points
OL-30644-01
Chapter 8 Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
Understanding Spanning Tree Protocol
Creating the Spanning-Tree Topology
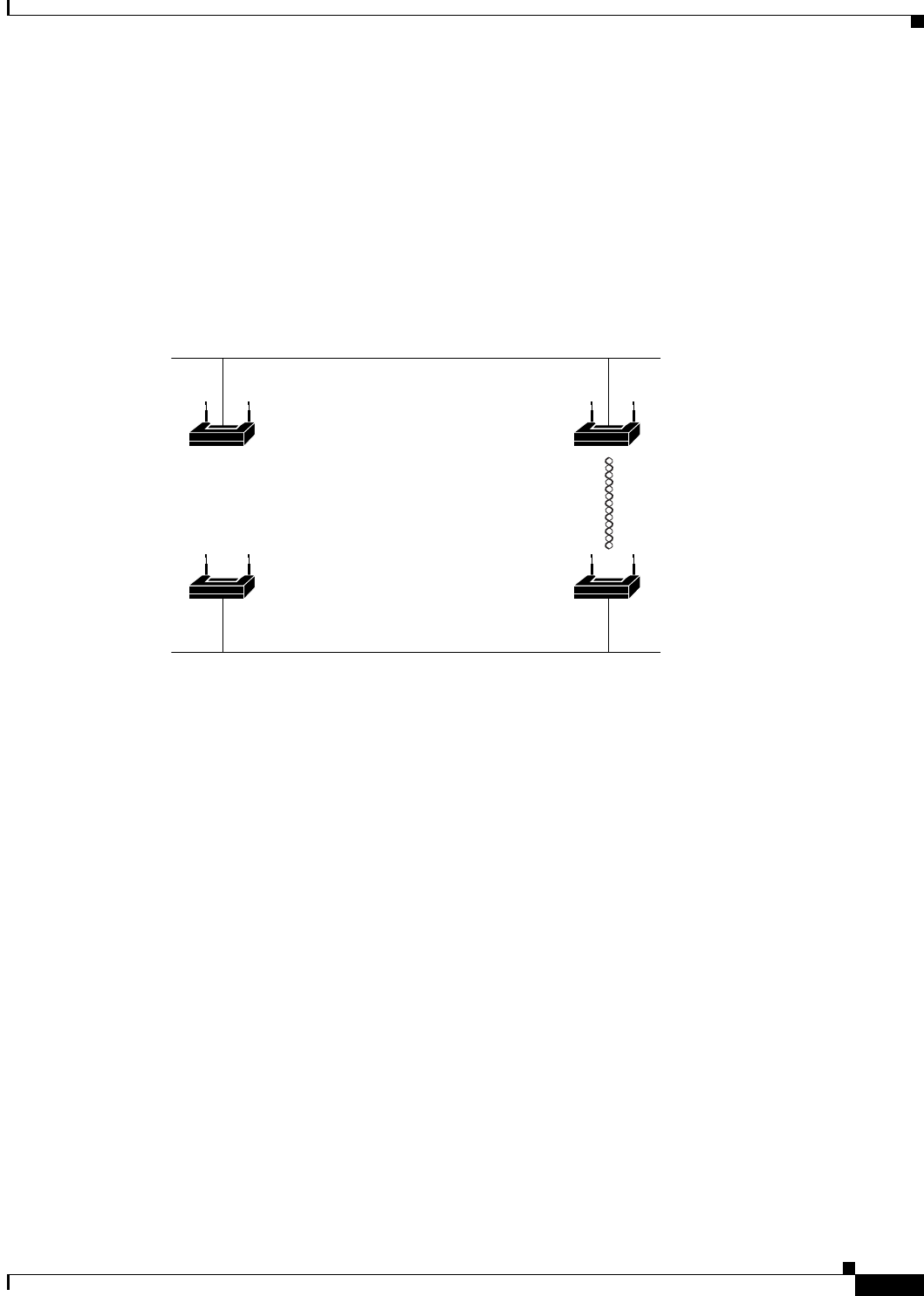
In Figure 8-1, bridge 4 is elected as the spanning-tree root because the priority of all the access
point/bridges is set to the default (32768) and bridge 4 has the lowest MAC address. However, because
of traffic patterns, number of forwarding interfaces, or link types, bridge 4 might not be the ideal
spanning-tree root. By increasing the priority (lowering the numerical value) of the ideal bridge so that
it becomes the spanning-tree root, you force a spanning-tree recalculation to form a new topology with
the ideal bridge as the spanning-tree root.
Figure 8-1 Spanning-Tree Topology
Spanning-Tree Interface States
Propagation delays can occur when protocol information passes through a wireless LAN. As a result,
topology changes can take place at different times and at different places in the network. When an
interface transitions directly from nonparticipation in the spanning-tree topology to the forwarding state,
it can create temporary data loops. Interfaces must wait for new topology information to propagate
through the LAN before starting to forward frames. They must allow the frame lifetime to expire for
forwarded frames that have used the old topology.
Each interface on a access point/bridge using spanning tree exists in one of these states:
• Blocking—The interface does not participate in frame forwarding.
• Listening—The first transitional state after the blocking state when the spanning tree determines
that the interface should participate in frame forwarding.
• Learning—The interface prepares to participate in frame forwarding.
• Forwarding—The interface forwards frames.
• Disabled—The interface is not participating in spanning tree because of a shutdown port, no link on
the port, or no spanning-tree instance running on the port.
An interface moves through these states:
• From initialization to blocking
LAN segment A
LAN segment B
Bridge 1
Bridge 3
Bridge 2
Bridge 4
56612