12-4
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points
OL-30644-01
Chapter 12 Configuring WDS, Fast Secure Roaming, Radio Management, and Wireless Intrusion Detection
Understanding Wireless Intrusion Detection Services
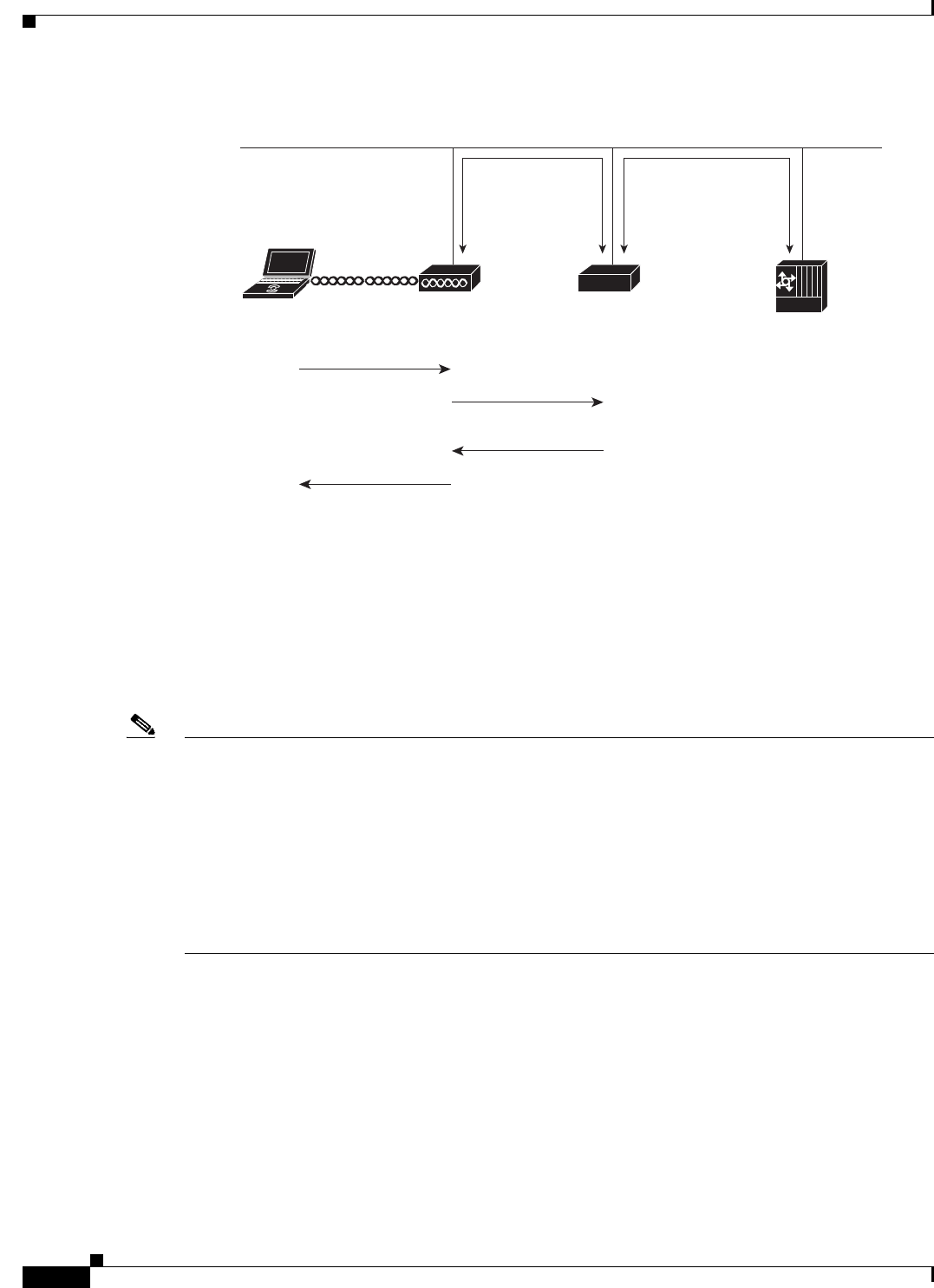
Figure 12-2 Client Reassociation Using CCKM and a WDS Access Point
The WDS device maintains a cache of credentials for CCKM-capable client devices on your wireless
LAN. When a CCKM-capable client roams from one access point to another, the client sends a
reassociation request to the new access point, and the new access point relays the request to the WDS
device. The WDS device forwards the client’s credentials to the new access point, and the new access
point sends the reassociation response to the client. Only two packets pass between the client and the
new access point, greatly shortening the reassociation time. The client also uses the reassociation
response to generate the unicast key. Refer to the “Configuring Fast Secure Roaming” section on
page 12-17 for instructions on configuring access points to support fast, secure roaming.
Note This mechanism also requires the client to accept the credentials that are being passed from one AP to
the other. Make sure that you enable CCKM on the access points, and also make sure that your wireless
client supports CCKM for the authentication mechanism (with CCX) used in your network. Without
CCKM support, the client may refuse the fast roaming mechanism and force a re-authentication through
the RADIUS server.
To know the CCX versions needed for each authentication mechanism, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/partners/pr46/pr147/program_additional_information_new_release_feature
s.html
To know the CCX version supported by each client type, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/web/partners/pr46/pr147/partners_pgm_partners_0900aecd800a7907.html
Understanding Wireless Intrusion Detection Services
When you implement Wireless Intrusion Detection Services (WIDS) on your wireless LAN, your access
points, and an optional (non-Cisco) WIDS engine work together to detect and prevent attacks on your
wireless LAN infrastructure and associated client devices.
Working with the (non-Cisco) WIDS engine, access points can detect intrusions and take action to
defend the wireless LAN.
WIDS consists of these features:
103569
Reassociation request
Reassociation response
Pre-registration request
Pre-registration reply
Roaming client
device
Access point Access point or switch
providing Wireless
Domain Services
Authentication server
Wired LAN
WDS


















