15-3
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points
OL-30644-01
Chapter 15 Configuring QoS
Understanding QoS for Wireless LANs
Regardless of the client support (or lack of support) for WMM, Cisco access points support WMM and
can be configured to provide wireless QoS in the downstream direction (from the AP toward the wireless
clients), and in the upstream direction when forwarding wireless frames to the wired interface.
Just as in other media, you might not notice the effects of QoS on a lightly loaded wireless LAN. The
benefits of QoS become more obvious as the load on the wireless LAN increases, keeping the latency,
jitter, and loss for selected traffic types within an acceptable range.
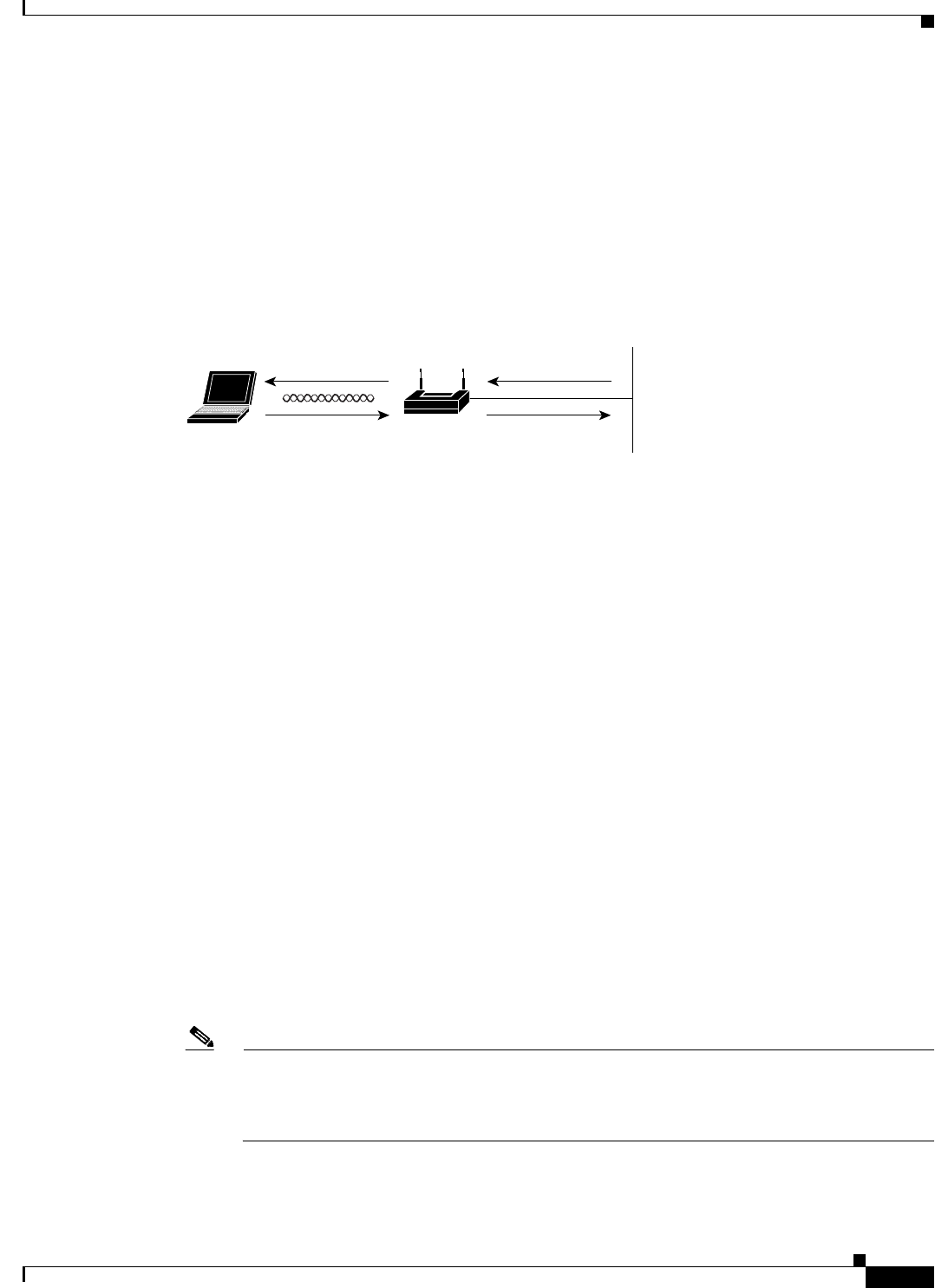
QoS on the wireless LAN focuses on downstream prioritization from the access point. Figure 15-1 shows
the upstream and downstream traffic flow.
Figure 15-1 Upstream and Downstream Traffic Flow
•
The radio downstream flow is traffic transmitted out the access point radio to a wireless client
device. This traffic is the main focus for QoS on a wireless LAN.
• The radio upstream flow is traffic transmitted out the wireless client device to the access point. Each
client independently determines what prioritization mechanisms should be used for this traffic. The
AP cannot force a prioritization mechanism for the client uplink traffic. However, the AP
configuration determines if uplink prioritization is allowed (when WMM is enabled on the AP
SSID) or disallowed (when WMM is disabled on the AP SSID).
• The Ethernet downstream flow is traffic sent from a switch or a router to the Ethernet port on the
access point. If QoS is enabled on the switch or router, the switch or router might prioritize and
rate-limit traffic to the access point.
• The Ethernet upstream flow is traffic sent from the access point Ethernet port to a switch or router
on the wired LAN. The access point does not prioritize traffic that it sends to the wired LAN based
on traffic classification. However, the AP maintains the traffic QoS marking.
Precedence of QoS Settings
When you enable QoS, the access point queues packets based on the Layer 2 class of service value for
each packet. The access point applies QoS policies in this order:
1. Packets already classified—When the access point receives packets from a QoS-enabled switch or
router that has already classified the packets with non-zero 802.1Q/P user_priority values, the access
point uses that classification and does not apply other QoS policy rules to the packets. An existing
classification takes precedence over all other policies on the access point.
Note Even if you have not configured a QoS policy, the access point always honors tagged 802.1P
packets that it receives over the radio interface and uses the matching 802.11e user priority queue
to send the packet over the air. You can use the Streams page to configure the rate at which each
queue should be sent and the number of retries for unicast packets.
Radio
downstream
Ethernet
downstream
Wired
LAN
Ethernet
upstream
Radio
upstream
Client
device
Access
point
81732


















