Getting Started Teledyne API - T100 UV Fluorescence SO2 Analyzer
64
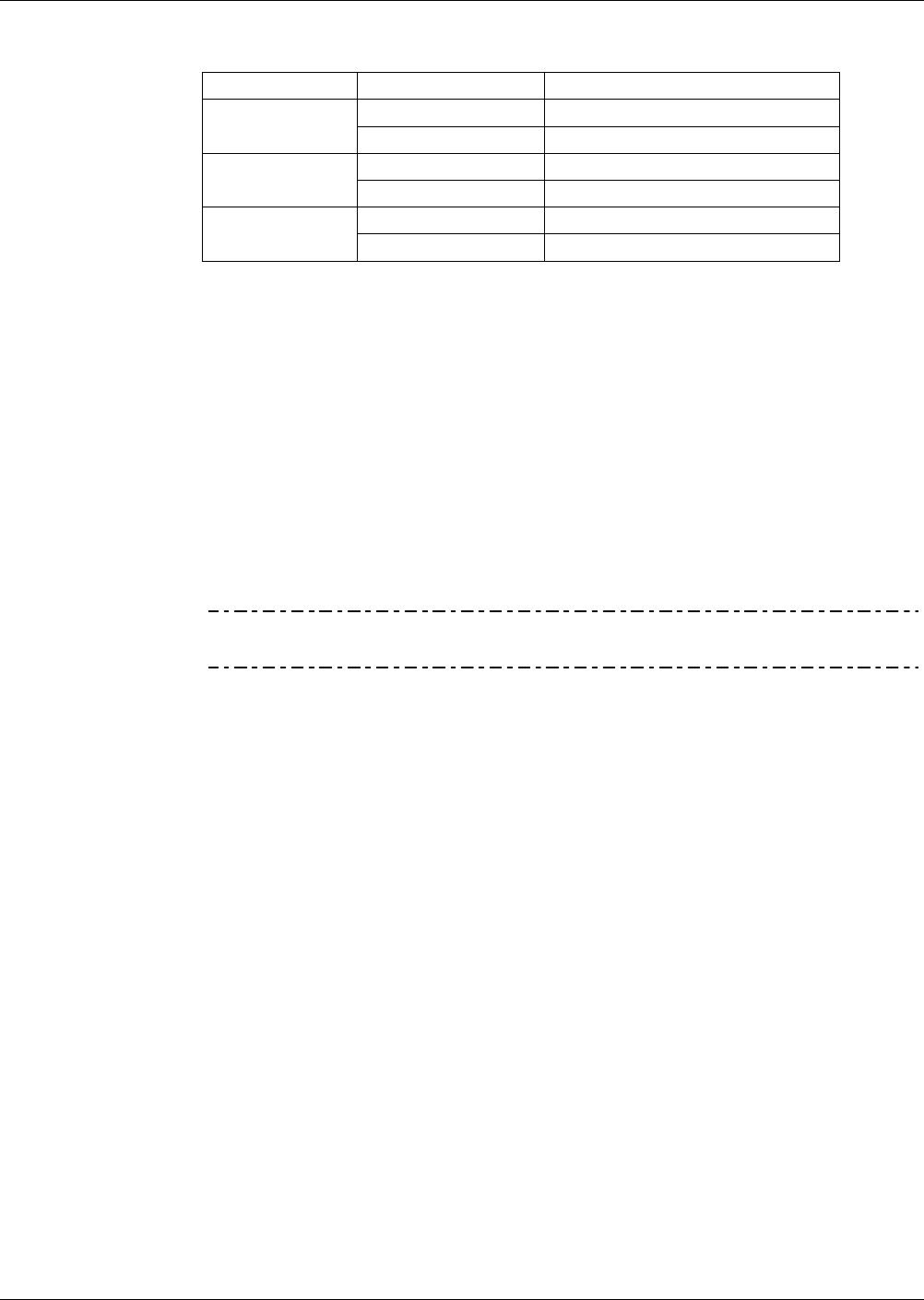
Table 3-11: IZS Valve Operating States
MODE VALVE CONDITION
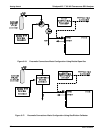
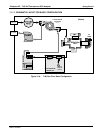
Sample/Cal Open to SAMPLE inlet
SAMPLE
Zero/Span Open to ZERO AIR inlet
Sample/Cal Open to zero/span valve
ZERO CAL
Zero/Span Open to ZERO AIR inlet
Sample/Cal Open to zero/span valve
SPAN CAL
Zero/Span Open to SPAN GAS inlet
The state of the IZS valves can also be controlled by any of the following means:
Manually from the analyzer’s front panel by using the SIGNAL I/O controls under
the DIAG Menu (refer to Section 5.9.1),
By activating the instrum
ent’s AutoCal feature (refer to Section 9.8),
Remo
tely by using the external digital control inputs (refer to Section 8.1.2 and
Section 9.7.1),
Rem
o
tely through the RS-232/485 serial I/O ports (refer to Appendix A-6 for the
applicable commands), or
Remotely via Ethernet
Note The permeation tube is not included in the IZS Option and must be
ordered separately. Refer to Section 1.4 for permeation tube options.
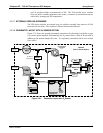
3.3.2.5. PERMEATION TUBE HEATER
In order to keep the permeation rate constant, the IZS enclosure is heated to a constant
50 C (10° above the maximum operating temperature of the instrument). The IZS heater
is controlled by a precise PID (Proportional/Integral/Derivative) temperature control
loop. A thermistor measures the actual temperature and reports it to the CPU for control
feedback.
The IZS option includes an external zero air scrubber assembly that removes all SO
2
the
zero air source. The scrubber is filled with activated charcoal.
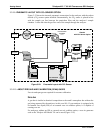
3.3.2.6. SPAN GAS CONCENTRATION VARIATION
Span gas is created when zero air passes over a permeation tube containing liquid SO
2
under high pressure, which slowly permeates through a PTFE membrane into the
surrounding air. The speed at which the SO
2
permeates the membrane is called the
effusion rate. The concentration of the span gas is determined by three factors:
Size of the membrane: The larger the area of the membrane, the more permeation
occurs.
Temperature of the SO
2
: Increasing the temperature of the increases the pressure
inside the tube and therefore increases the effusion rate.
Flow rate of the zero air: If the previous two variables are constant, the permeation
rate of air into the zero air stream will be constant. Therefore, a lower flow rate of
06807C DCN6650