DEFINITY ECS Release 8.2
Administrator’s Guide
555-233-506
Issue 1
April 2000
Managing data calls
422Wideband Switching
15
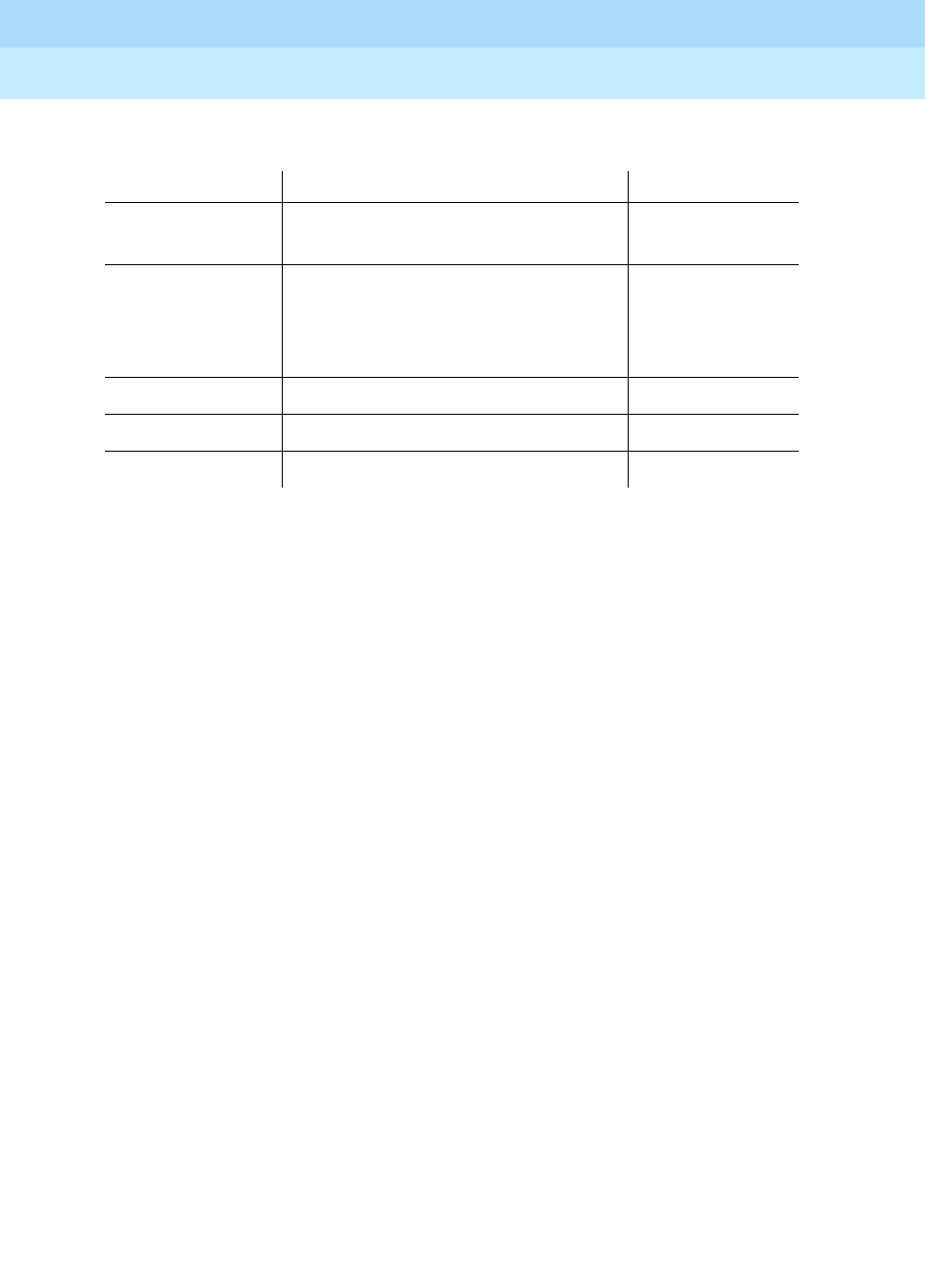
The following table provides information on Wideband Switching channel types.
Channel allocation
For standard narrowband communication, ISDN-PRI divides a T1 or E1 trunk as
follows:
■ T1 trunks are divided into 23 information channels are 1 signaling channel
■ E1 trunks are divided into 30 information channels, 1 signaling channel,
and 1 framing channel
Certain applications, like video conferencing, require greater bandwidth. You can
combine several narrowband channels into one wideband channel to
accommodate the extra bandwidth requirement. DEFINITY ECS serves as a
gateway to many types of high-bandwidth traffic. In addition, DS1 converters are
used for wideband switching at remote locations.
Performed using one of the three allocation algorithms: fixed, flexible, or floating.
■ Fixed allocation — Provides contiguous-channel aggregation. The starting
channel is constrained to a predetermined starting point. (Used only for H0,
H11, and H12 calls.)
■ Flexible allocation — Allows a wideband call to occupy non-contiguous
positions within a single T1 or E1 facility (NxDS0).
■ Floating allocation — Enforces contiguous-channel aggregation. The
starting channel is not constrained to a predetermined starting point
(NxDS0).
Channel Type Number of Channels (DSOs) Data Rate
H0 (T1 or E1) 6 (grouped 4 (T1) or 5 (E1) quadrants
of 6 B-channels each)
384 Kbps
H11 (T1 or E1) 24 (on T1 - all 24 B-channels, with
the D-channel not used; on E1 -
B-channels 1 to 15, and 17 to 25, and
B-channels 26 to 31 unused)
1536 Kbps
H12 (E1 only) 30 (B-channels 1 to 15 and 17 to 31) 1920 Kbps
NxDS0 (T1) 2-24 128–1536 Kbps
NxDS0 (E1) 2-31 128–1984 Kbps


















