63-3
User Guide for Cisco Security Manager 4.4
OL-28826-01
Chapter 63 Configuring Quality of Service
Quality of Service on Cisco IOS Routers
Understanding Marking Parameters
Marking parameters enable you to classify packets, which entails using a traffic descriptor to categorize
a packet within a specific group. This defines the packet and makes it accessible for QoS handling on
the network. Both traffic policers and traffic shapers use the packet classification to ensure adherence to
the contracted level of service agreed upon between the source and your network. Additionally, marking
parameters enable you to take packets that might have arrived at the device with one QoS classification
and reclassify them. Downstream devices use this new classification to identify the packets and apply
the appropriate QoS functions to them.
Security Manager uses two types of marking for IPv4 packets—one based on IPP classes and one based
on DSCP values. IPP is based on the three most significant bits in the Type of Service (ToS) byte of each
packet, which means you can partition traffic into eight classes. For historical reasons, each precedence
value corresponds with a name, as defined in RFC 791. Table 63-1 on page 63-3 lists the numbers and
their corresponding names, from least to most important.
Note Classes 6 and 7 are generally reserved for network control information, such as routing updates.
DSCP is based on the six most significant bits in the ToS byte (the remaining two bits are used for flow
control), with values ranging from 0 to 63. The DSCP bits contains the IPP bits, which makes DSCP
backward-compatible with IPP.
Marking is generally used on devices that are close to the network edge or administrative domain so that
subsequent devices can provide service based on the classification mark.
For information about defining marking parameters in a QoS policy, see Defining QoS Class Marking
Parameters, page 63-15.
Related Topics
• Understanding Queuing Parameters, page 63-4
• Understanding Policing and Shaping Parameters, page 63-6
• Defining QoS Policies, page 63-10
• Quality of Service on Cisco IOS Routers, page 63-1
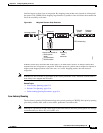
Table 63-1 IP Precedence Classes
Class Name
0 routine
1priority
2 immediate
3flash
4 flash-override
5 critical
6internet
7network