14-5
User Guide for Cisco Security Manager 4.4
OL-28826-01
Chapter 14 Managing TrustSec Firewall Policies
Overview of TrustSec Firewall Policies
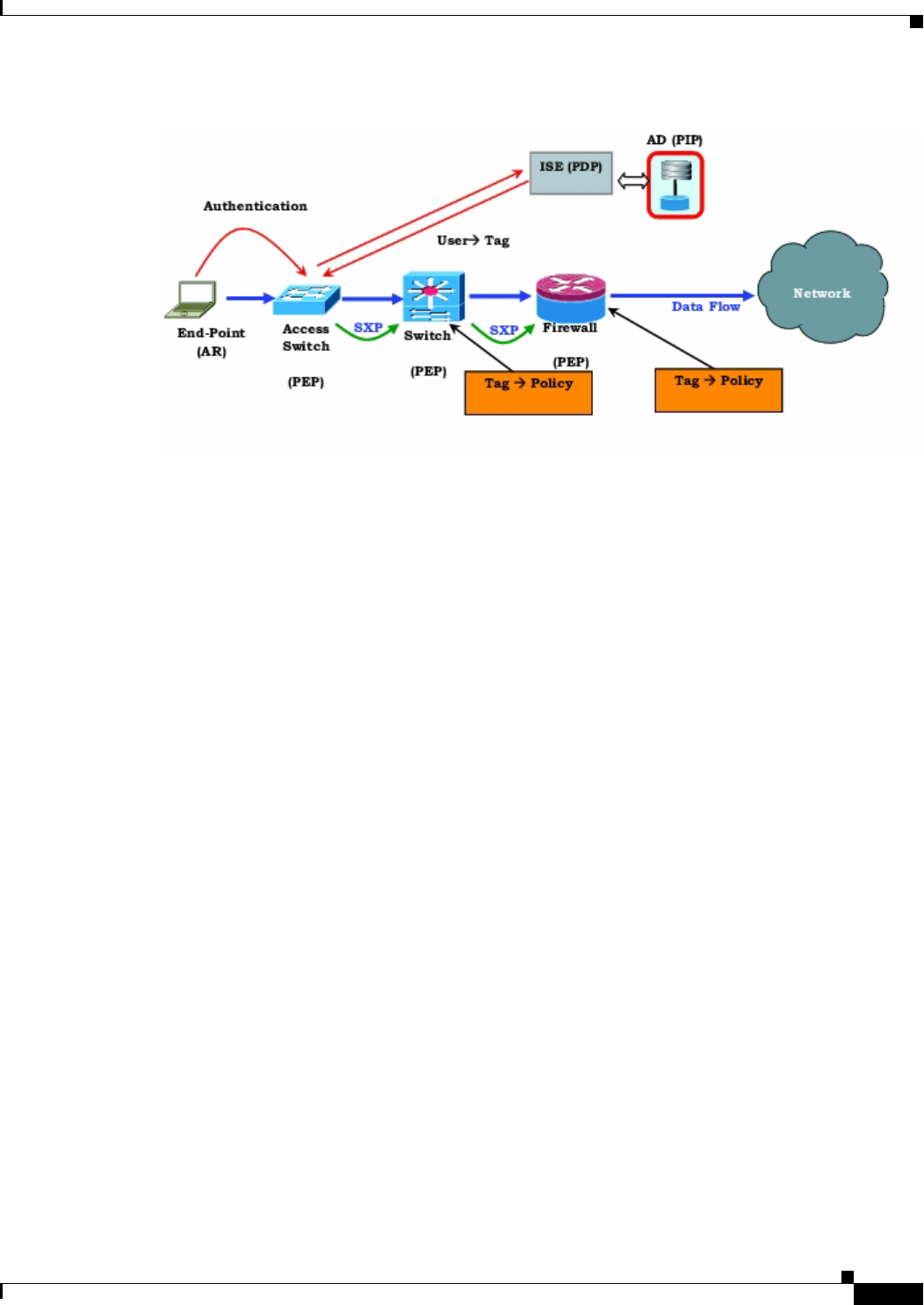
Figure 14-2 Security Policy Enforcement
1. An end-point device connects to an access layer device directly or via remote access and
authenticates with Cisco TrustSec.
2. The access layer device authenticates the end-point device with the ISE by using authentication
methods such as 802.1X or web authentication. The end-point device passes role and group
membership to classify the device into the appropriate security group.
3. The access layer device uses SXP to propagate the IP-SGT mapping to the upstream devices.
4. The ASA receives the packet. Using the IP-SGT mapping passed by SXP, the ASA looks up the
SGTs for the source and destination IP addresses.
If the mapping is new, the ASA records it in its local IP-SGT Manager database. The IP-SGT
Manager database, which runs in the control plan, tracks IP-SGT mappings for each IPv4 or IPv6
address. The database records the source from which the mapping was learned. The peer IP address
of the SXP connection is used as the source of the mapping. Multiple sources can exist for each
IP-SGT mapping.
If the ASA is configured as a Speaker, the ASA transmits all IP-SGT mappings to its SXP peers. See
About Speaker and Listener Roles, page 14-6.
5. If a security policy is configured on the ASA with that SGT or security group name, the ASA
enforces the policy. (You can create security policies on the ASA that contain SGTs or security
group names. To enforce policies based on security group names, the ASA needs the security group
table to map security group names to SGTs.)
If the ASA cannot find a security group name in the security group table and it is included in a
security policy, the ASA considers the security group name unknown and generates a system log
message. When it becomes know after the ASA refreshes the security group table from the ISE, the
ASA generates a system log message indicating that the security group name is known.


















